Boviet Solar opens solar production facility in North Carolina
With an investment reportedly approaching $400 million, the manufacturing plant will be built in two phases with phase one producing 2 GW of solar modules and phase two expected to produce 2 GW of solar cells in 2026.
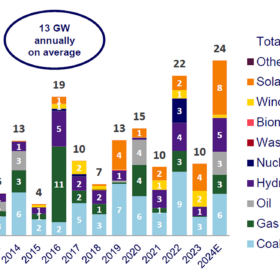
US solar industry to add 502 GW (DC) of capacity in next decade
Wood Mackenzie warns that policy uncertainty could significantly alter its projections for US solar industry growth. The research firm says the US solar industry will add 502 GW (DC) of capacity over the next decade, with annual installations surpassing 40 GWdc through 2035.
Are robots coming for solar installer jobs?
Robots on solar sites are not new; they have been deployed to automate everything from operations and maintenance to inspection and cleaning. In recent months, there has been an uptick in interest in robots for installation, particularly among utility-scale solar developers dealing with staff shortages, safety concerns, rising costs, and pressure to build.
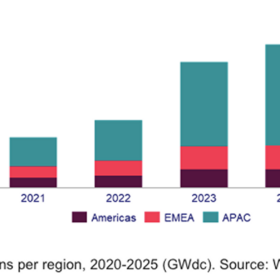
South America estimated to add 160 GW of PV by 2034
Mature markets Brazil and Chile will account for 78% of total installations, with small-scale projects (<5 MW) accounting for 48% of total builds in the region, according to Wood Mackenzie.
China installed 8 GW of solar in ‘Belt and Road’ countries in 2024
Wood Mackenzie says Chinese companies installed 24 GW of power projects throughout the world under China’s “Belt and Road” development initiative in 2024. This marked a record for a calendar year, with solar projects accounting for about one-third of the newly installed capacity.
Wood Mackenzie predicts solar growth will stagnate in 2025
Wood Mackenzie’s latest report forecasts that 493 GW (DC) of solar will be added throughout the world this year, compared to 495 GW in 2024. Solar module prices are expected to rise this year as manufacturers aim to recover profit losses from the past two years.
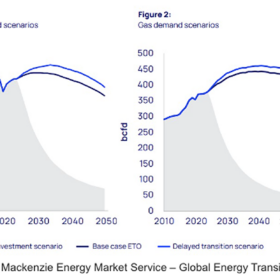
Wood Mackenzie warns of upstream sector impact from delayed transition
Wood Mackenzie says that a 30% increase in upstream spending will be needed to meet stronger oil and gas demand under a delayed energy transition. The research firm warns that this scenario could strain supply chains, inflate costs, and push Brent crude prices above $100/barrel by the 2030s.
Australia’s batteries surf revenue wave on back of volatile power prices
Investments in battery storage within Australia’s National Electricity Market (NEM) are increasingly profitable due to higher power price volatility and changing market dynamics, according to the latest report by Wood Mackenzie. Going forward, four-hour storage systems are projected to have fastest return on investment.
US starts solar cell manufacturing to close supply chain gap
The “US Solar Market Insight Q4 2024” report, published by the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA) and Wood Mackenzie, states that domestic module manufacturing will be able to match the rapid pace of growth in the US solar industry, with cell production also ramping up.
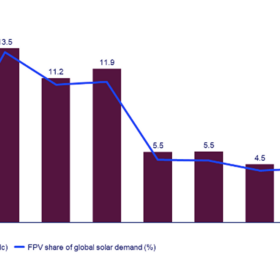
Wood Mackenzie forecasts 77 GW of floating solar by 2033
Wood Mackenzie predicts that the global floating solar market will be dominated by the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region and led by India, China and Indonesia through to 2033. The consultancy says growth will be driven by rising demand, decreased capital expenditure and supportive policies.