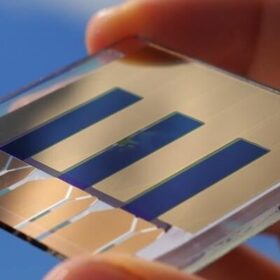
Fraunhofer ISE unveils 15.8%-efficient organic solar cell
Germany’s Fraunhofer ISE has achieved a world record efficiency for organic cells at the lab level. It now aims to bring the PV technology to market maturity.
Binary organic solar cell achieves 19,31% efficiency
Hong Kong Polytechnic University researchers have developed a binary organic solar cell (OSC) with a record power conversion efficiency of 19.31%. They invented a non-monotonic intermediate state manipulation strategy to lower the non-radiative recombination loss and boost efficiency.
Weekend Read: New turf for thin films
Thin-film technologies have long promised to make a major impact on the solar industry but have largely been constrained to niche applications and research labs if they were not shredded by the market. After several false starts, current trade dynamics and promising research programs may help solar thin films find their place in the sun.
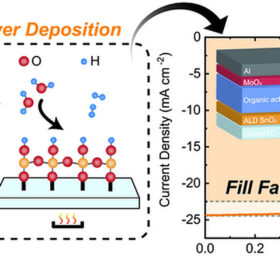
Tin oxide-based organic solar cell hits 17.26% efficiency, 79% fill factor
Dutch scientists have used atomic layer deposition to build an organic solar cell with a tin oxide electron transport layer. This improved electron mobility and transparency, resulting in a record fill factor.
Semi-transparent organic photovoltaics for greenhouse applications
Scientists from the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), have used an antioxidant known as L-glutathione as an interlayer in an organic PV cell to prevent other materials from oxidizing. The cell has an efficiency of 13.5% and an average visible transmittance of 21.5%. The researchers said it is suitable for applications in solar greenhouses.
MIT scientists produce new organic photovoltaic fabrics
US researchers have developed a thin-film organic solar module on a vapor-deposited releasable substrate made of parylene. The device could be used as a wearable fabric, or to bring solar generation to remote locations.
Transparent organic PV materials for solar window applications
US scientists have built photovoltaic materials with two top layers made of phthalocyanine and heptamethine. They tested the new tech across four different climate areas in the United States.
PV-driven rechargeable control module for ‘cyborg cockroaches’
Japanese researchers have built ultra-soft PV devices and ultra-thin electronics that can be placed on the curved abdomens of cockroaches without affecting their mobility. The system can be used to monitor hazardous areas, or for urban search-and-rescue operations.
Large-area organic solar cell with 14.7% efficiency
Scientists in Korea built an organic solar cell that is reportedly able to prevent aggregation in photoactive layers. The device could be used for applications in buildings, vehicles, and the Internet of Things.
Femtosecond lasers for high-efficiency organic PV
UK scientists have developed a process using laser and x-ray pulses to observe what happens in the initial fractions of a second after light hits a solar cell. By applying the technique to various organic PV materials, they expect to gain insights that could quickly the improve the efficiency of such materials.