Solar could hold advantage in post-pandemic global energy sector
The International Energy Agency has acknowledged dramatic falls in energy investment caused by the Covid-19 crisis but said renewables, including PV, offered an attractive proposition to investors as the dust settled, given their enticing economics and short turnaround times.
Covid-19 weekly round-up: Residential systems in Italy will get a 110% tax rebate and UK consumers are being paid to turn appliances on as coronavirus turns the energy world upside down
Plus, Australia’s Greens want renewables front and center of the post Covid-19 economy and Mexican plant owners are overturning a politically-motivated ban on clean energy, however, Indian developer Acme solar says pandemic delays warrant it reneging on the terms of the record-low solar price agreement it signed.
Sunny regions could see one-cent solar within a decade
The solar learning curve usually applied to panel costs has been extrapolated to the larger, non-module element of the price of solar electricity generated by big projects, leading one commentator to predict new solar projects could be cheaper than legacy fossil fuel plants within 10-15 years in certain markets.
Covid-19 weekly briefing: Evidence abounds of renewable energy gains at the expense of fossil fuels as the clamor for a green recovery rises
Portugal set a new coal-free record because of the pandemic as Belgium and Israel moved to help the renewables industry. But there was grim news in Mexico and Turkey, and Bangladeshi clean energy firms have appealed for more assistance.
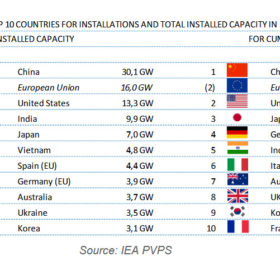
Global PV capacity additions hit 115 GW in 2019, says IEA
In terms of new solar installations, China was the world’s largest PV market for the third year in a row with 30.1 GW of fresh capacity in the 12 months to the end of December, followed by the United States with 13.3 GW and Japan with 7.7 GW.
Solar, wind and hydro resilient during Covid-19 crisis
A study by the International Energy Agency into the chilling effect of the Covid-19 pandemic on energy demand states renewables will be ‘the only energy source likely to experience demand growth for the rest of 2020’. The slower the economic recovery, the more the fossil fuel industry will suffer.
Could Covid-19 be the catalyst for change where the COP process has stalled?
While the world’s climate negotiators dither, the post Covid-19 world could see their efforts overtaken – but only if policymakers are bold enough to take the opportunity to offer truly green fiscal stimulus packages to get us through the crisis. Felicia Jackson, from the center for sustainable finance of the School of Oriental and African Studies at the University of London, gives her thoughts here.
European Investment Bank signs hydrogen investment deal
The EIB and the Hydrogen Council aim to jointly develop new ways to generate funding for hydrogen projects under the European Commission’s InnovFin Advisory program. The two parties, however, have not disclosed the financial terms of their planned collaboration.
Commercial rooftops will lead renewables growth in the next five years
Although the International Energy Agency’s latest renewables report forecasts impressive solar growth there is still a nagging feeling it has produced conservative estimates and the emphasis on sharing costs with grid operators is predictable.
Mali gold mine set for 30 MW of solar and 13.5 MWh of storage
Two German companies will develop one of the largest off-grid PV and storage projects to date. The low cost of the technology and expense of conventional generators is likely to see the hybrid plant recover its costs in three to seven years.