Siemens, ABB invests in Norwegian battery company
Startup Morrow Batteries has raised €100 million ($105.9 million) in a funding round led by Siemens and ABB. It will use the money to build its first battery cell factory in Norway, its home market.
UK group developing floating organic flow battery storage project
MSE international and its partners have concluded the feasibility study for an organic large-scale flow battery project in Portsmouth, England. The 650 kW/6.1 MWh project might end up having have a lower levelized cost of electricity than lithium-ion or vanadium redox flow batteries.
The mobility rEVolution: Nissan, Mitsubishi launch mini EVs for Japan
In other news, Tesla expands Supercharger access for other EV brands in Europe, Hong Kong gets its first universal ultra-rapid charging station, and BMW invests in Canadian company Mangrove to back sustainable lithium metal production.
Australia’s consumer watchdog warns about LG home batteries
The Australian Competition and Consumer Commission has issued a call for homeowners to check their residential energy storage systems, amid a national recall of that batteries due to concerns about overheating.
Greenko starts work on 5.23 GW wind-solar-storage project in India
Indian developer Greenko has started building a hybrid energy storage project with 10.8 GWh of daily pumped storage, 3 GW of solar, and 550 MW of wind.
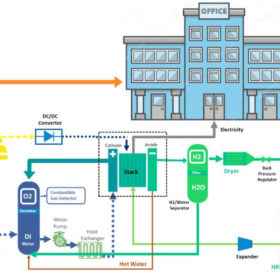
Cost comparison between lithium batteries, fuel cells, reversible solid oxide cells as storage for off-grid rooftop PV
Scientists in the United Arab Emirates have looked at how off-grid rooftop PV could be combined with batteries, fuel cells or reversible solid oxide cells for energy storage. The modeling assumed a typical commercial building in Los Angeles.
Origin secures approval for 2,800 MWh battery in Australia
Origin Energy has secured planning approval for a 700 MW/2,800 MWh grid-connected battery to be developed at the site of its coal-fired Eraring power station in the Australian state of New South Wales.
Storage-linked 5 MW floating PV plant goes online in Portugal
Portuguese utility EDP has switched on a new 5 MW floating solar array at the Alqueva hydropower dam.
Smarter E products at a glance
pv magazine summarizes the products we covered at the recent Smarter E exhibition, in the first of a series of reports on all of the new releases from the annual trade fair in Munich, Germany.
Emissions-free battery recycling facility will use electricity rather than smelting
ACE Green Recycling has announced plans to build a new plant in Texas to recycle both lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries.