Blackouts and high utility prices are driving solar and storage adoption in the US, SunPower survey says
The survey of 1,500 homeowners shed light on the home solar energy experience and motivating factors behind solar purchases.
Redox flow battery retains more than 90% of capacity over 6,000 cycles via new catholyte
The battery was built with a new catholyte and a symmetry-breaking strategy, which consists of changing the symmetry of the redox-active organic molecules instead of using the common approach of attaching a hydrophilic functional group.
The weekend read: China’s battery storage awakening
China’s efforts to shift electricity generation from a coal-dominated system to a greener mix of renewables is not only centered on wind, solar and other technologies – the country is also rapidly pursuing energy storage. Vincent Shaw reports from Shanghai.
Energy storage appears to be fully charged for exponential growth
Lithium-based energy storage volumes are expected to grow by multiple orders of magnitude in the coming years, with a 1,000% capacity increase by 2023.
Grid-scale storage potential in India
A new study provides a novel assessment of grid-scale storage deployment in India, both in the near term and the long term. Scenario-based capacity expansion modeling shows when, where and how much storage can be cost-effectively deployed in India through 2050.
Novel salt solution for lithium-ion battery fires
Australian researchers have tested a novel lithium salt for high-voltage lithium batteries in electric vehicles and grid-scale storage systems. They claim the salt is less hazardous than conventional battery materials.
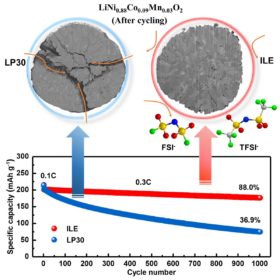
Lithium-metal battery with capacity retention of 88% over 1,000 cycles
German scientists have applied a new combination of cathodes and electrolytes to improve the stability of lithium-metal batteries. They fabricated a device with an energy density of 560 watt-hours per kilogram and a Coulombic efficiency of 99.94%.
SMA warns of electronic component shortage
In the first half of the year, the German PV inverter maker recorded high demand for its inverters and storage solutions from the residential solar segment. The effects of the corona pandemic, however, have had an impact on the commercial segment and, although a recovery in demand is expected in the second half of the year, SMA said it is currently dealing with delivery issues.
Canadian Solar posts solid Q2 results, lowers 2021 shipment guidance
The solar PV module manufacturer reported strong growth for its energy storage business and an overall 105% year-on-year turnover growth. Its total module production capacity reached 19.7 GW at the end of June.
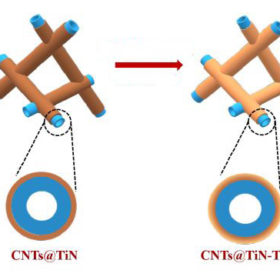
Lithium-sulfur battery with shorter charging time, longer lifespan
Japanese scientists have developed a new lithium-sulfur battery by using titanium oxide and titanium nitride to prevent the formation of polysulfides during the fabrication process. This allows the battery to retain 85% of its capacity after 500 cycles at 2 C.