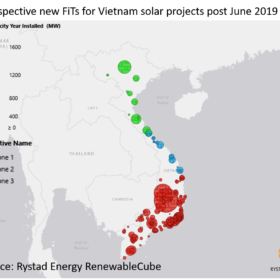
Vietnam mulls multi-layered FIT scheme as it kicks energy transition into gear
With its feed-in tariff set to expire at the end of June, Vietnam is considering different levels of payment, classified across three irradiation regions and involving four solar technologies. Future payments would range from $0.0659-0.0985/kWh, with the cloudy north in line for the highest tariffs and with the government likely to revise tariffs for new projects every two years.
2019 PV installations to hit 123 GW, global balance shifting, says IHS Markit
More predictions from IHS Markit reveal that 123 GW of solar PV installations are expected in 2019 – up 18% on the capacity additions expected this year. It also sees a market shift away from China, with two thirds of capacity located elsewhere. The overcapacity situation is also expected to ease.
ADB invests $155 million in Thai green bonds
The bank continues its involvement in Thailands largest IPP B.Grimm, which is set to grow its renewable energy portfolio. According to ADB, the green bond proceeds will go to nine operational solar PV plants with a cumulative rating of 67.7 MW, and 30.8 MW that are currently still under construction.
Vietnam should increase solar FIT to $0.15/kWh, report says
According to a report published by the Asian Development Bank (ADB), key factors such as the low-regulated price of electricity and uncertainty of the creditworthiness of Vietnam’s state-owned utility EVN are making it difficult to develop bankable solar and RE projects. An improved fiscal energy policy is recommended as the only way to provide the local energy sector with long-term capital and competence in conducting green credit appraisal. Furthermore, the report warns that the current 20-year FIT of US$0.0935/kWh for solar projects is too low.
Sungrow bags 201 MW solar project in Vietnam
The Chinese-based manufacturer has closed a deal for the supply of its inverter solutions to the large-scale solar project in southern Vietnam. Sungrow says it has deployed a total of 1 GW of solar projects in Vietnam.
Juwi signs contract for third project in Vietnam
German renewables developer Juwi has signed a contract to provide EPC services for a 50 MW project located near to the coast in central Vietnam’s Binh Dinh province. This project brings Juwi’s pipeline in the Southeast Asian country to 130 MW.
IRENA and southeast Asian nations pledge action on PV
The International Renewable Energy Agency wants to unlock the PV potential of the Asia-Pacific region with technical and planning support. It says a better flow of knowledge is needed to close the gap on a regional aim of generating 23% of energy from renewables by 2025.
Asian market to see 355 GW of solar over five years, despite policy challenges
Despite political hurdles in key markets including China, India and Japan, Asia remains highly active. This year, 59 GW of solar is expected to be installed and due to further system price declines, a phase-out of subsidy schemes can be offset.
Floating PV to splashdown in Vietnam
A 47.5 MW floating solar power plant is being planned by Vietnamese hydropower producer Da Mi, a unit of Vietnamese power utility Electricity of Vietnam (EVN), at one of its water reservoirs in the south of the country. The Asian Development Bank is now considering financing the project. Meanwhile, Sharp has announced the completion of a 48 MW ground-mounted PV facility in the Eastern Asian country.
Vietnam extends provincial FiT scheme – with caveats
The government has extended the payment system in Ninh Thuan by 12 months. But with a 2 GW cap and 1.9 GW in place already, new entrants may have to move fast.