Canadian startup unveils residential air source heat pump for cold climates
Terravis Energy said its heat pump prototype uses difluoromethane (R32) as the refrigerant and has a seasonal coefficient of performance (SCOP) of approximately 3.0 under Ontario’s environmental conditions.
New model to predict defrost cycles, behavior of air-sourced heat pumps in cold weather
UK-based researchers have developed a novel method to estimate the amount of defrost cycles a heat pump will experience in the winter and how much energy it would require to implement the cycles. The results of their simulation showed a strong relationship between the number of defrost cycles and the ambient temperature.
First attempt to build back-contact micrometric III-V photovoltaic cells
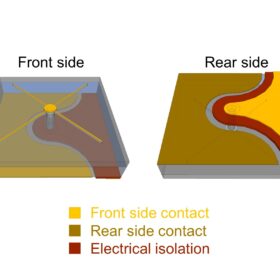
An international research group has utilized through-substrate-vias to create 3D interconnections in III-V solar cells with a triple-junction architecture. The novel cell design was found to have a low shading factor of below 3% and a 6-fold increase in wafer area use compared to cells based on 2D interconnects.
Gallium arsenide solar cell achieves 23.1% efficiency via electrochemical porosification
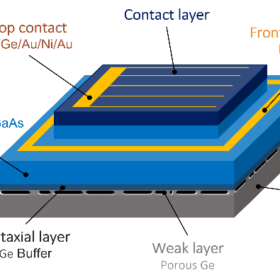
An international research group has utilized a new porosification technique to build gallium arsenide (GaAs) solar cells that allow the recovery of germanium films. The new cell achieved an efficiency that is reportedly in line with that of other GaAs PV devices, but can be produced at a lower cost thanks to the reuse of germanium.
Weekend Read: The fruitful search for other thin films
First Solar and its cadmium telluride (CdTe) technology dominate thin-film solar in the mainstream market. Valerie Thompson looks at the US-based business and the future of thin-film PV technology.
Laser-sharp focus on interconnections
As the world’s solar manufacturers continue to ramp up production at an eye-watering speed, a cell connection technique up to 10 times faster than the industry standard holds rich promise, according to Keven Tremblay, from Canadian laser process specialist Laserax.
The Hydrogen Stream: FNB Gas presents hydrogen network plan for Germany
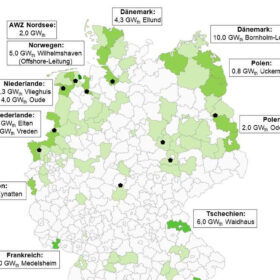
FNB Gas has unveiled plans for a hydrogen core network in Germany, while Tree Energy Solutions has started working on an electrolyzer and 1 GW of renewable energy assets in Canada.
Strategies to develop ‘solar neighborhoods’
A group of scientists across the world have created a list of recommendations that can help create solar neighborhoods. In a recently published study they highlight the importance of legislative frameworks and advanced computing.
Canada’s largest behind-the-meter solar project
Construction has started on two solar projects in the Canadian province of Alberta, including one with a flow battery energy storage system.
The Hydrogen Stream: Japan backs hydrogen in aviation
The Japanese government has confirmed to pv magazine that it is launching a new support scheme for hydrogen in aviation, while Japanese investors continue to actively pursue participation in a green ammonia project in South Africa.