Photovoltaic and solar thermal energy production and wind energy production
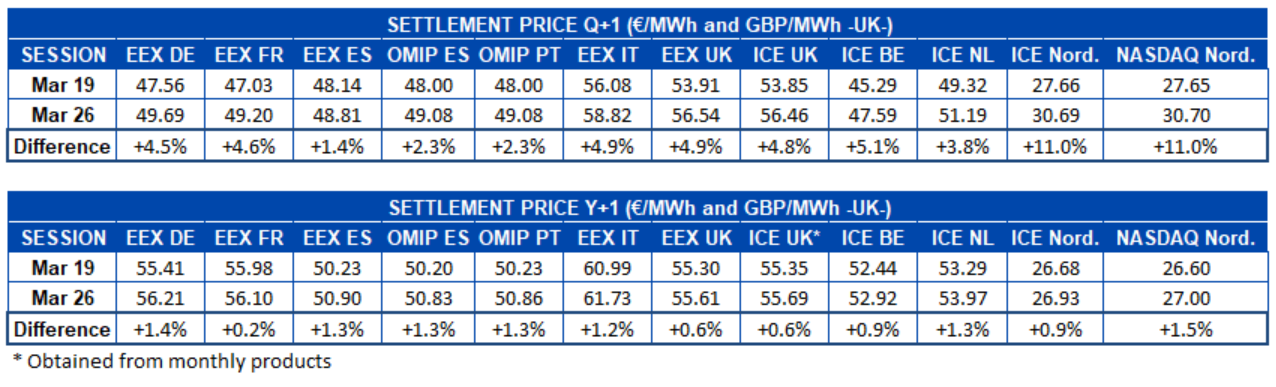
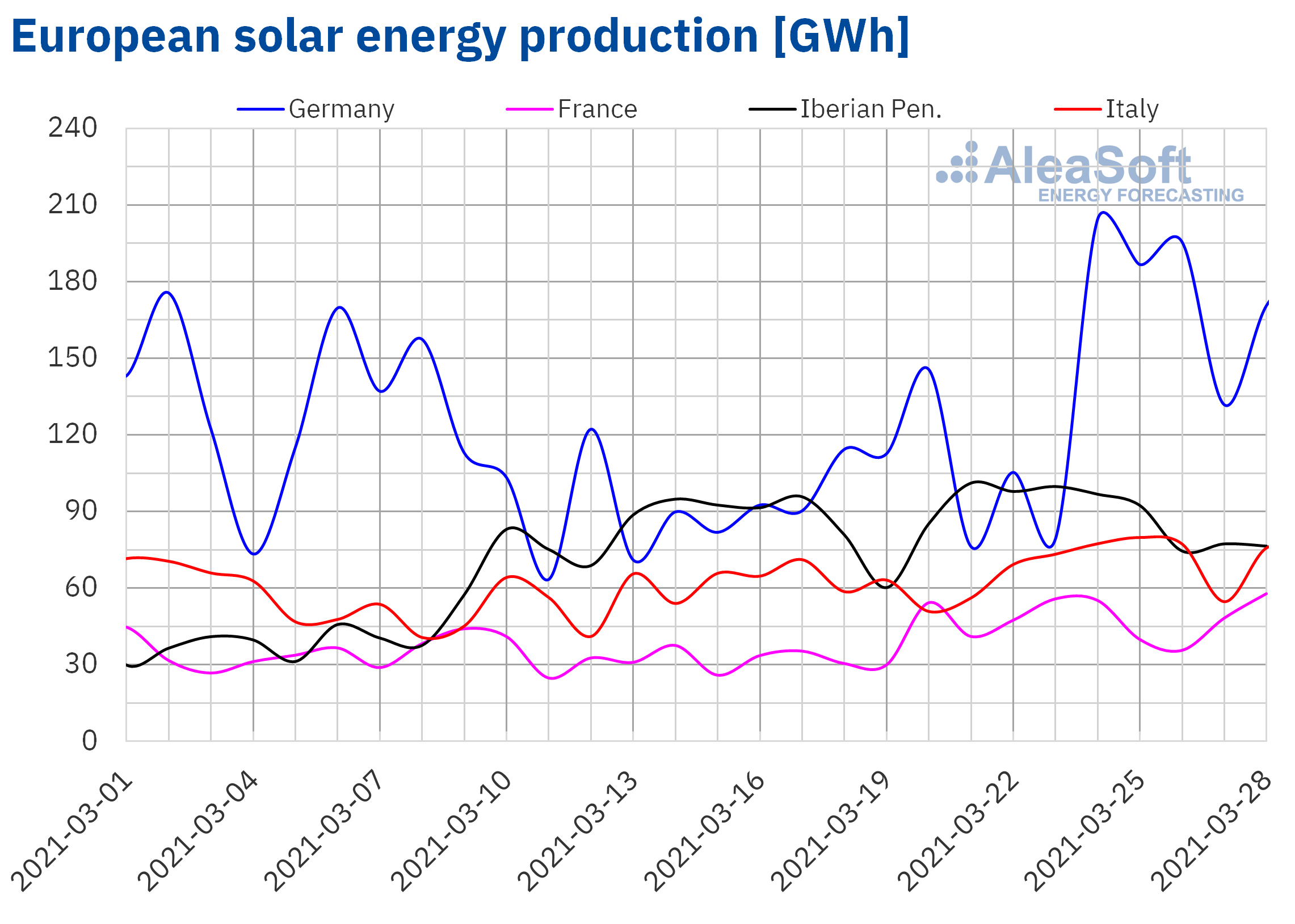
The solar energy production increased in all markets during the week that began on March 22 compared to the previous week, except in the Portuguese market, where it decreased by 7.6%. In the German market, the solar energy production was 50% higher, while in the French and the Italian markets the growth was 36% and 18% respectively. In the Spanish market, the solar energy production, which in this case includes the photovoltaic and the solar thermal technologies, also grew, although only by 2.0%.
For the week that began on Monday, March 29, the AleaSoft‘s solar energy production forecasting indicates that it will decrease in the Spanish market and in the Italian market. On the contrary, an increase in production with this technology is expected in the German market.
 Source: Prepared by AleaSoft using data from ENTSO-E, RTE, REN, REE and TERNA.
Source: Prepared by AleaSoft using data from ENTSO-E, RTE, REN, REE and TERNA.
 Source: Prepared by AleaSoft using data from ENTSO-E, RTE, REN, REE and TERNA.
Source: Prepared by AleaSoft using data from ENTSO-E, RTE, REN, REE and TERNA.
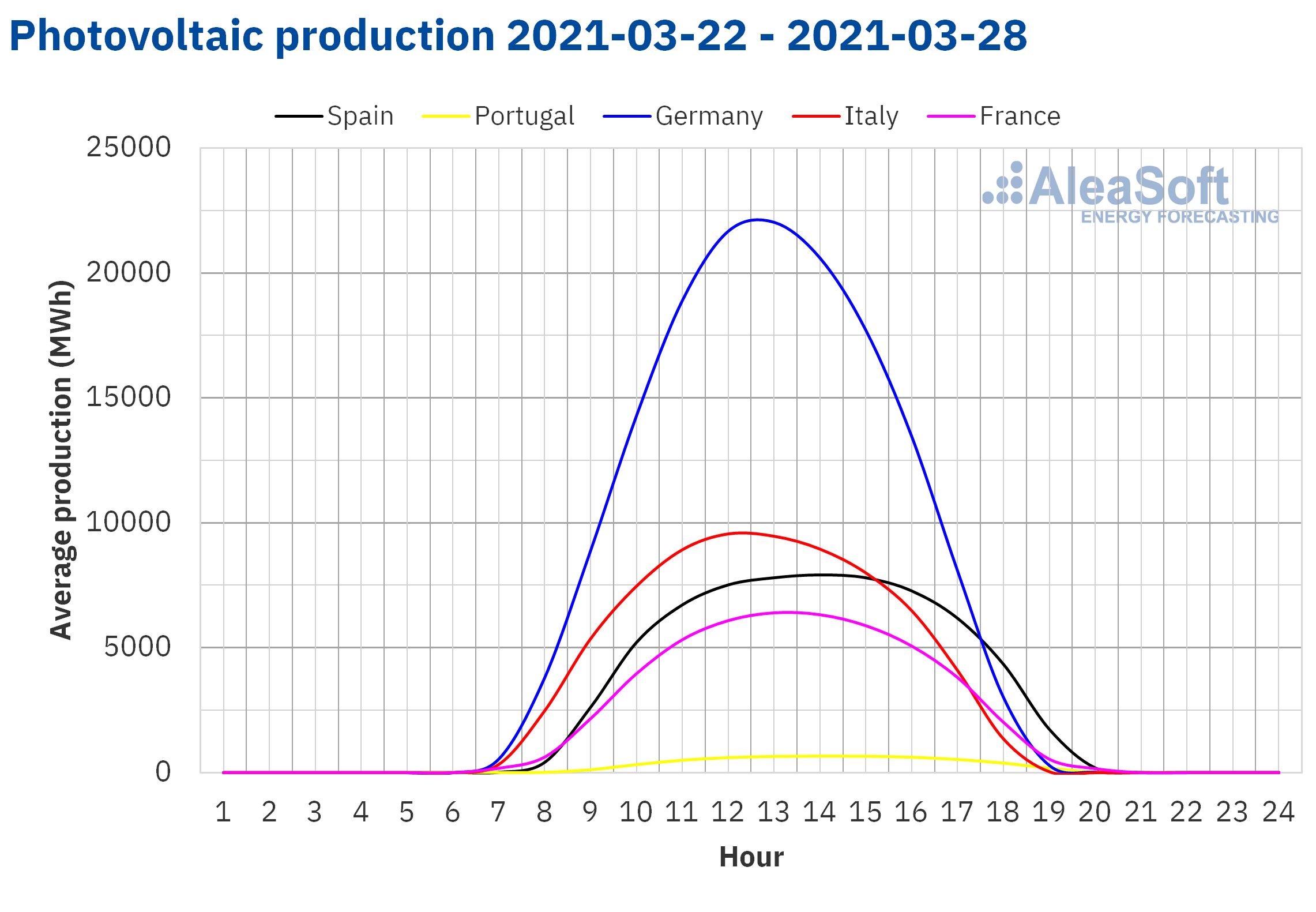
On the contrary, during the fourth week of March, the wind energy production fell compared to the previous week in almost all the markets analysed at AleaSoft. In the Iberian Peninsula, the production with this technology fell by 64%, while in the French market it fell by 40% and in the German market by 1.7%. The exception was the Italian market in which there was an increase of 12%.
For the week that started on March 29, the AleaSoft‘s wind energy production forecasting indicates that it will increase compared to that of the third week of March in all the markets analysed at AleaSoft, except in the Italian market, where a reduction of the production with this technology is expected.
 Source: Prepared by AleaSoft using data from ENTSO-E, RTE, REN, REE and TERNA.
Source: Prepared by AleaSoft using data from ENTSO-E, RTE, REN, REE and TERNA.
Electricity demand
The electricity demand fell in a generalised way in all European markets in the week of March 22 compared to the previous week. One of the main reasons for this decrease was the rise of more than 2.0 °C in average temperatures in most markets. In France and Great Britain, the greatest drops in demand were registered, which were higher than 8.0% in both territories.
For the week of March 29, the AleaSoft‘s demand forecasting indicates that it will continue to decrease in most European markets. An increase in average temperatures and a decrease in work activity due to the festivities associated with Holy Week in some markets are expected, which will contribute to this decrease.
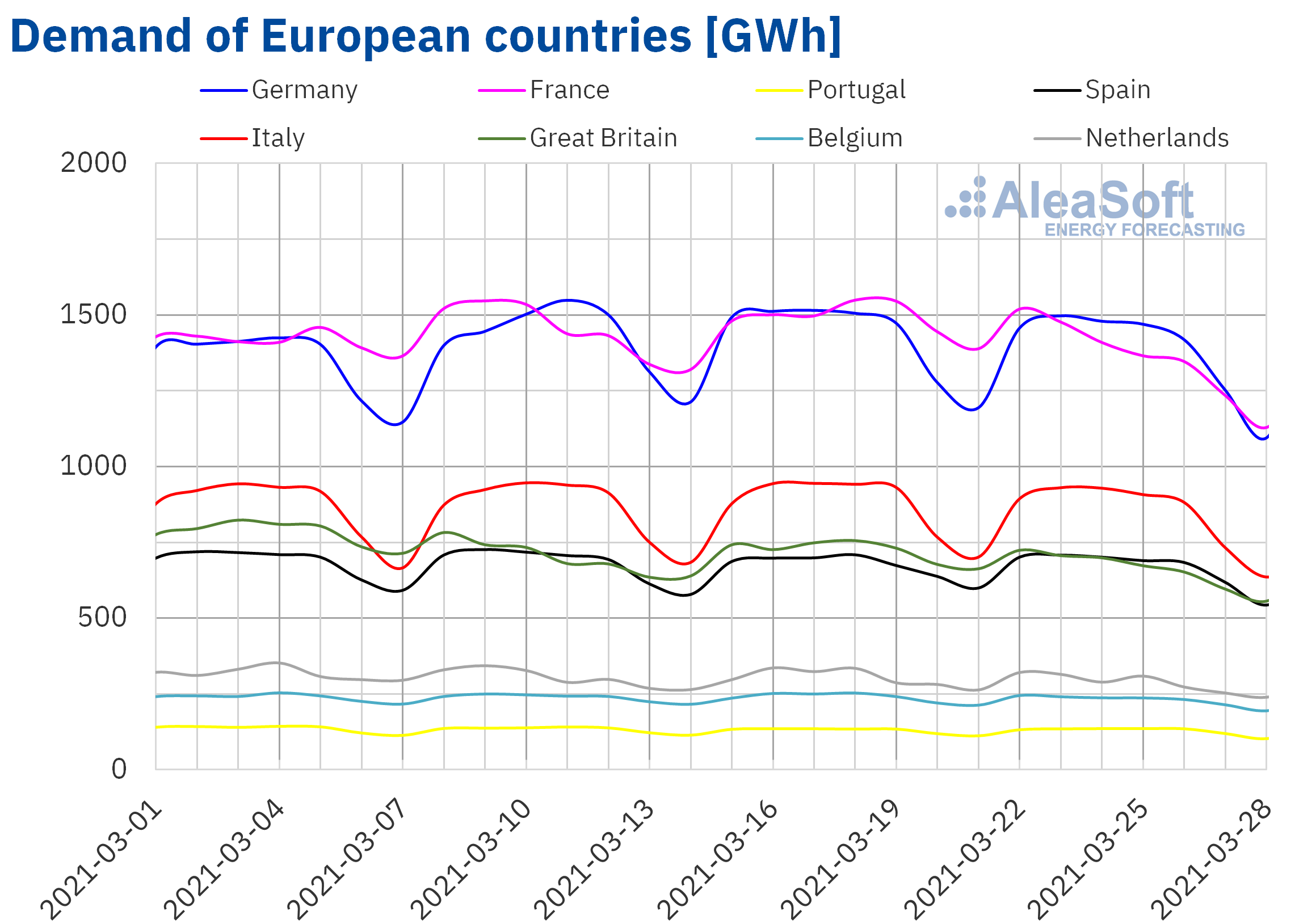 Source: Prepared by AleaSoft using data from ENTSO-E, RTE, REN, REE, TERNA, National Grid and ELIA.
Source: Prepared by AleaSoft using data from ENTSO-E, RTE, REN, REE, TERNA, National Grid and ELIA.
European electricity markets
The week of March 22, the prices of most of the European electricity markets analysed at AleaSoft fell compared to those of the previous week. However, in the MIBEL market of Spain and Portugal, there were significant price increases, of 83% and 82% respectively. The prices also rose in the IPEX market of Italy, but in this case only by 1.4%. On the other hand, the largest drop in prices, of 21%, was that of the Nord Pool market of the Nordic countries, followed by that of the N2EX market of the United Kingdom, of 17%. In the rest of the markets, the price decreases were between 3% of the EPEX SPOT market of France and 14% of the EPEX SPOT market of the Netherlands.
In the fourth week of March, the highest weekly average price was that of the IPEX market, of €62.76/MWh, followed by that of the British market, of €57.12/MWh. While the lowest average was that of the Nordic market, of €30.81/MWh. In the rest of the markets, the prices were between €46.70/MWh of the market of the Netherlands and €55.92/MWh of the Spanish market.
On the other hand, on Saturday, March 27, negative hourly prices were reached in the markets of Germany, Belgium and the Netherlands. On Sunday, March 28, in addition to these markets, there were also negative hourly prices in France. The lowest price, of ‑€57.63/MWh, was reached at the hour 13 of Saturday, March 27, in the Belgian market. This hourly price is the lowest in the Belgian market since April 2020.
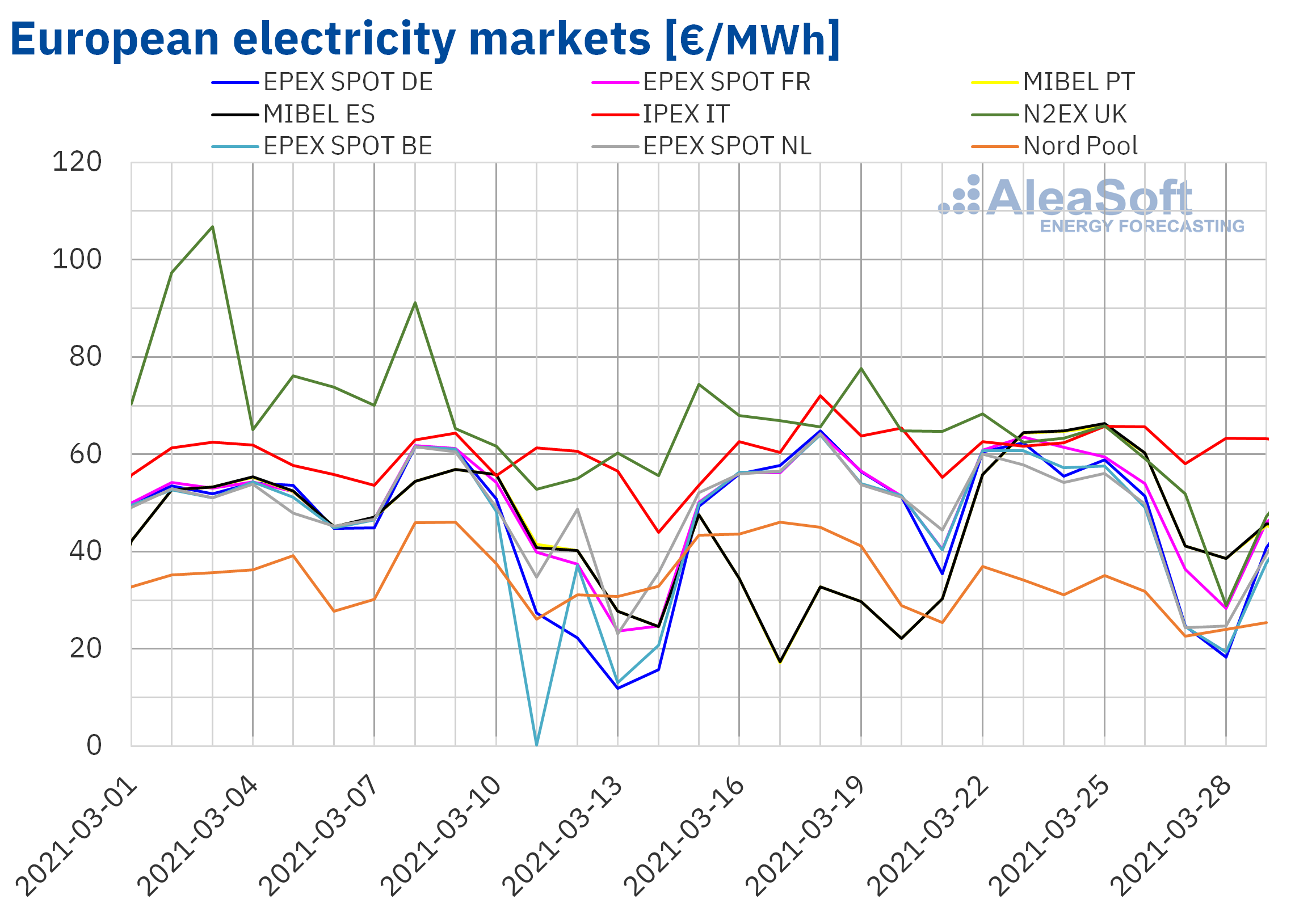 Source: Prepared by AleaSoft using data from OMIE, EPEX SPOT, N2EX, IPEX and Nord Pool.
Source: Prepared by AleaSoft using data from OMIE, EPEX SPOT, N2EX, IPEX and Nord Pool.
During the fourth week of March, the general decrease in demand and the increase in solar energy production in almost all European electricity markets allowed the prices to fall in most markets. The slight decrease in CO2 prices also contributed to this trend. However, the significant drop in wind energy production in the Iberian Peninsula favoured the rise in prices in the MIBEL market.
The AleaSoft‘s price forecasting indicates that the week of March 29 there will be generalised price declines thanks to the recovery of the wind energy production in most markets and the decrease in electricity demand due to the increase in temperatures and the decrease of labour during Holy Week.
Electricity futures
At the end of the fourth week of March, in the session of Friday 26, the electricity futures prices for the second quarter of 2021 registered a general increase compared to the same day of the previous week, Friday 19. The NASDAQ market and the ICE market, both of the Nordic countries, were those that led the increases with an increase of 11%, after rising more than €3/MWh, with which they also led the statistics in absolute terms. The EEX market of Spain was the one with the lowest variation, with a rise of 1.4%. In the rest of the markets, the increases were between 2.3% of the OMIP market of Spain and Portugal and 5.1% of the ICE market of Belgium.
Something similar, but on a smaller scale, occurred for the product of the next year 2022 in all the European electricity futures markets analysed at AleaSoft. The NASDAQ market of the Nordic countries registered the largest increase, with a 1.5% rise, followed closely by the EEX market of Germany, with 1.4%. The market with the lowest variation in this product was the EEX of France, with 0.2% and in general in the rest of the markets the increases were between 0.6% and 1.3%.
Brent, fuels and CO2
During the fourth week of March, the Brent oil futures prices for the month of May 2021 in the ICE market ranged between $64.62/bbl of March 22 and $60.79/bbl of March 23. The largest daily variation, of 6%, occurred on Wednesday, March 24, influenced by fears about problems in the supply levels. Last Tuesday, March 23, the Suez Canal was blocked due to a large ship that was stranded. This created uncertainty about possible delays in the deliveries of fossil fuels, such as oil or gas, transported by sea. On March 29, the ship was partially refloated and, according to the responsible authorities, the work to restore traffic in the canal is expected to end that day.
On the other hand, the next OPEC+ meeting to agree on its production levels as of May is scheduled on April 1, which will also exert its influence on the evolution of the prices in the coming days.
As for the TTF gas futures in the ICE market for the month of April 2021, the fourth week of March followed a generally upward trend. As a result, the settlement price of Friday, March 26, was €18.70/MWh, 8.3% higher than that of the previous Friday and the highest since the first half of January.
Regarding the settlement prices of the CO2 emission rights futures in the EEX market for the reference contract of December 2021, on Monday, March 22, they reached the weekly maximum settlement price of €42.84/t. However, during the fourth week of March, there were price declines that allowed a settlement price of €40.35/t to be registered on Thursday, March 25, which was 4.9% lower than that of the previous Thursday. On the other hand, on Friday, March 26, the prices recovered to €41.73/t.
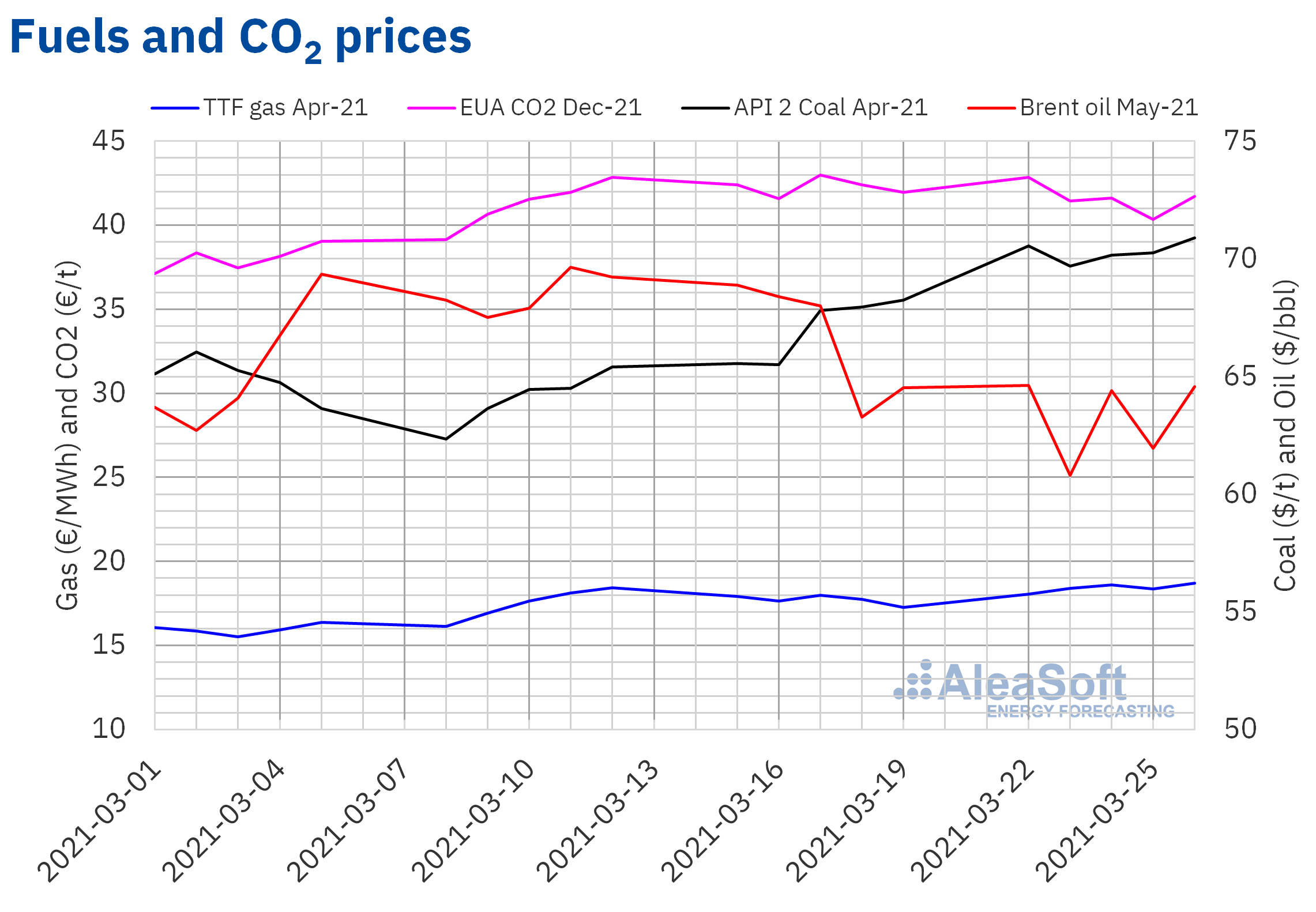 Source: Prepared by AleaSoft using data from ICE and EEX.
Source: Prepared by AleaSoft using data from ICE and EEX.
The importance of the short‑term forecasting
When making the offers for the daily, intraday and adjustment markets, it is necessary to have electricity markets prices forecasts, for, based on the expected prices, optimising the offers in order to maximise the profits. These forecasts are also useful for planning both the industrial production and the power generation of the manageable technologies, as well as the storage with batteries. The short‑term prices forecasts take into account the behaviour of the market in recent days and use as input, among many others, the demand forecasting and the production forecasting by technologies, including the wind energy and the solar energy, which are generated taking take into account updated weather forecasts. The expected behaviour in periods such as Easter and Christmas is another element that is taken into account when making these forecasts.
Having a global vision of the variables of the spot and futures electricity markets, the fuels markets and the CO2 emission rights markets is necessary to understand their dynamics and detect causalities in different periods. The AleaApp Platform is a tool that brings together the data from the main energy markets and other variables such as the macroeconomic data and includes various options to facilitate the information analysis and help in the digitalisation of the companies, providing a centralised source of energy markets data.