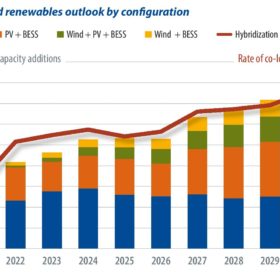
Hybrid systems in demand
The past two decades have seen a boom in solar, driven by falling costs and rising efficiencies, with global capacity additions reaching 176 GW in 2021. Most PV generating capacity added to date has been standalone projects, driven by subsidies, tenders and the drive for the lowest levelized cost of electricity (LCOE). But as the penetration rate of standalone solar increases, so does the potential for a negative impact on power markets and network stability, writes Jason Sheridan of IHS Markit.
New government, new targets
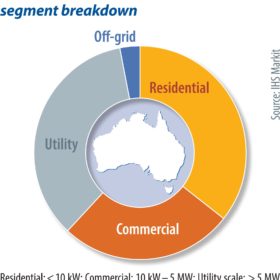
IHS Markit has increased its solar installation forecast for Australia to 45 GW between this year and 2030, following the recent election which saw the country vote in the Labor Party. Climate-focused candidates won a majority in May, with plans to invest in grid upgrades to facilitate the development of Renewable Energy Zones (REZs) and community solar-plus-storage projects. IHS Markit’s Clare McCarrick writes that solar installations will support the new government’s target of a 43% emissions reduction by 2030, based on 2005 levels. This is a significant increase on the previous government’s target of a 26% to 28% reduction.
Strong case for energy storage, despite rising costs
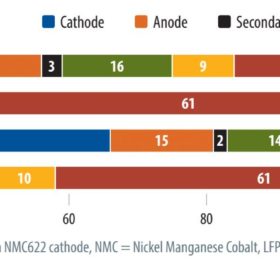
Unprecedented volatility in global commodity markets, disruption to logistics and supply chains, and unrelenting growth has driven up the cost of Li-ion batteries since the middle of 2021. Sam Wilkinson and Oliver Forsyth of IHS Markit expect to see rapid manufacturing expansion that will still struggle to keep up with demand, and ultimately lead to the establishment of a smaller group of battery-makers specialized in supplying stationary energy storage systems.
Local expansions counter tracker disruption
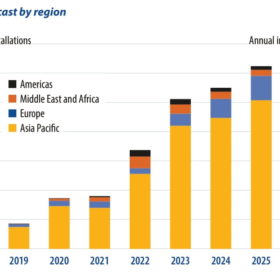
The solar tracker market experienced significant challenges during 2021, writes Jason Sheridan of IHS Markit, with major price increases and availability disruption across raw materials and delays to global freight operations. Despite these challenges, global solar tracker shipments grew to over 50 GW in 2021, representing 15% year-on-year growth. This was driven by strong demand in key markets such as the United States, Spain, mainland China, Brazil, and Chile. Solar tracker installations are expected to reach over 46 GW in 2022, an increase of 20% compared to 2021.
Asia takes the lead on floating PV
Floating PV is consolidating as a growth segment for PV demand, mainly driven by supportive policies and incentives extended by governments across the world. A major reason for this push is the limited land availability in many markets. Despite higher equipment prices compared to ground-mounted installations, developers see the opportunity to save on land and O&M costs. The output can also be as much as 30% higher than a ground-mount PV plant, depending on the site and technology used.
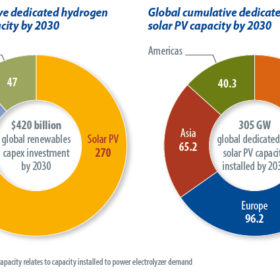
The green hydrogen prize
IHS Markit Senior Research Analyst Jason Sheridan looks at the potential pitfalls of an energy carrier that could generate almost $420 billion of investment in renewables this decade.
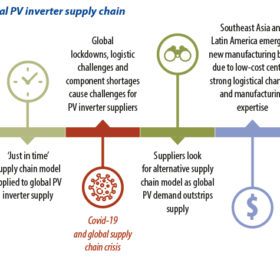
Inverter makers go global
A combination of booming demand, supply chain bottlenecks, and energetic moves by politicians to bring manufacturing “back home” is persuading solar inverter manufacturers to set up fabs in whole new global zip codes, as IHS Markit’s Shaunagh Moodie and Siqi He report.
Building back better
The United States set new plans for the energy transition and climate change after President Joe Biden took office, setting the nation on a path to achieving its ambitious goals with legislation related to renewable energy deployment. Albert Hsieh, a researcher at PV InfoLink, explores the various factors affecting solar development in the United States and the possible impacts on the PV industry if the Build Back Better Act is passed.
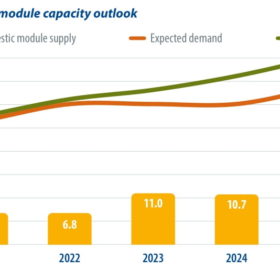
Keeping up with growing demand
Despite a few recent bumps in the road, the outlook is bright for the solar industry in 2022 and beyond. A growing list of countries are making commitments to net-zero carbon emissions, and solar energy is central to many of their strategies for reaching this goal. InfoLink analyst Amy Fang sheds light on the growing demand for PV around the world, and the latest price trends and technology developments that will shape the market in 2022.
EVA Outlook
Encapsulant film is a key material that determines the quality and lifespan of modules. The film is used in module encapsulation, during which solar cells are assembled into the space between the glass and backsheet and laminated into place. Like many other PV module components, encapsulant materials have been in short supply recently, and longer capacity expansion times mean that supplies of EVA, the most commonly used material, will remain tight this year. InfoLink’s Derek Zhao takes a closer look.