Exceeding all expectations
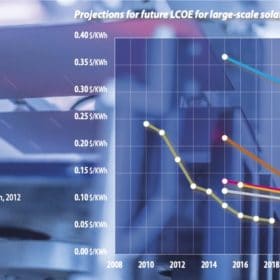
Forecasts for the levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) of solar PV were hotly contested over the past decade, with one trend predominating: All but the most optimistic outlooks were wrong. pv magazine has gathered data to showcase the recent evolution of solar PV energy costs, and the results are stark. Within just a few years, initial projections become outdated, which means that forecasts of solar PV prices are more art than science.
New EU battery rules support a sustainable industry
On Dec. 10, European Internal Market and Environment Commissioners Thierry Breton and Virginijus Sinkevičius, in conjunction with Vice President Maroš Šefčovič, announced a keenly anticipated piece of legislation: the commission’s proposal for modernized EU battery rules. Pia Alina Lange – head of communications for Recharge, the European battery industry association – says that while there are potential pitfalls with the new regulation, it could pave the way to sustainable industry development.
From minnow to colossus
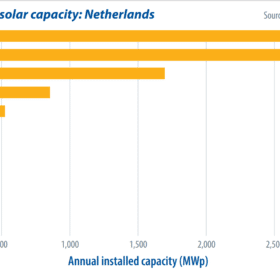
When looking at European Union renewable energy statistics, the Netherlands was, and still is in many ways, the laughingstock of Europe. But in recent years the country has come to rank near the top in solar deployments. In 2021 this small nation may even surpass neighboring Germany with new installed capacity. Rolf Heynen, the CEO of Dutch New Energy Research, takes a look at what is going on.
Korea shifts into top gear
There is a fresh sense of urgency and common purpose in South Korea toward combating climate change. In 2021, government mandates to boost green energy are being well received among many Korean blue-chip companies. This bodes well for the nation’s solar PV rollout, writes Ian Clover, manager of corporate communications at Q Cells.
New applications, surging demand
China’s project development segment is dynamic, to say the least. Having undergone significant changes toward a “subsidy-free” footing, developers are now facing requirements to integrate storage, deploy hybrid arrays, and pursue self consumption through BIPV and agrivoltaics applications, writes Frank Haugwitz, the director of the Asia Europe Clean Energy (Solar) Advisory (AECEA).
Politicians tend to overpromise, except when it comes to solar
The speed of all transitions is inherently underestimated, and solar PV is no exception. The EU has grossly underestimated its coming of age, as its forecasts for 2020 were off by 67% for the Netherlands and 74% for Germany, writes Rolf Heynen, CEO of Dutch New Energy Research.
Indonesia’s coal exit plan
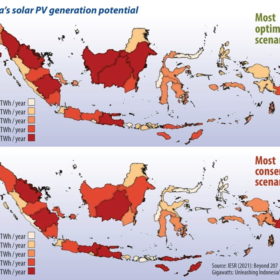
Indonesia, the second-biggest coal exporter in the world, is now taking more steps to reduce its dependency on “black gold” as it starts to consider clean energy.
EV race heats up
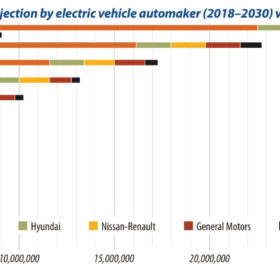
The race to electrify passenger cars is picking up pace, writes Prachi Mehta, senior research analyst for Wood Mackenzie. Competition among leading EV automakers is fierce, as 2024 looms as a watershed year when auto battery-pack prices cross a key consumer threshold.
Trolley car conundrum
The U.S. solar industry faces a moral dilemma, writes Paula Mints of SPV Market Research. Either continue to deploy projects and set aside concerns about forced labor in China’s Xinjiang region, or source PV cells and modules from elsewhere, while bearing higher costs, in the pursuit of urgent action against climate change.
More sun for everyone
It turns out that you can have too much of a good thing, says Mark Byrne of Australia’s Total Environment Centre. Or rather, it’s possible that there is too much rooftop PV at some times in some places. As a result, a range of critical reforms – including the introduction of export tariffs to pay for upgrades of the electricity distribution network – are necessary to allow for the uninhibited growth of solar in the future, he argues.