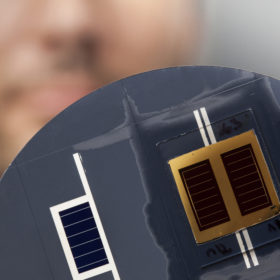
Swiss researchers team with NREL to break 35% cell efficiency
A collaborative project between the U.S. National Renewable Energy Laboratory, the Swiss Center for Electronics and Microtechnology (CSEM) and the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) has tested a range of multi junction cells in tandem configuration, and achieved efficiencies of up to 35.9%.
Dutch researchers model perovskite performance
A team of researchers at the Netherlands’ AMOLF institute has modelled the performance of tandem perovskite/silicon solar cells under real-world climate conditions, and found that the tandem cells are little more efficient than the Si cell alone. The research shows, however, that if correctly optimized, this type of cell could perform at efficiency levels above 38%.
BIPV: Researchers develop solar glass blocks to power houses
Researchers at the UK’s Exeter University have created solar cell-embedded glass bricks, which in addition to generating electricity let in natural light and provide thermal insulation.
1366 Technologies, Hanwha Q Cells hit 20.3% cell efficiency with Direct Wafer process
U.S. based PV innovator 1366 Technologies, and Korean PV manufacturer Hanwha Q CELLS have announced a new performance record for cells produced using 1366’s Direct Wafer technique. The cells achieved 20.3% efficiency, which has been independently confirmed by Fraunhofer ISE.
Haitian energy entrepreneurs call for investment security
At an international PV conference held in the Haitian capital Port-au-Prince, companies were demanding improvements to the political framework for the development of solar power in the country. Additionally, calls were made for low interest loans for private individuals, to cover initial investment in a PV system.
IRENA: Renewable energy can meet a quarter of India’s energy demand
As India’s energy needs are rising fast, the increased use of renewables in 2030 could save the economy 12 times the installation costs, when reduced environmental and health damage are taken into account, shows International Renewable Energy Agency’s roadmap to 2030, ranking solar as the country’s second largest source of renewable energy.
Haiti inaugurates the largest smart-grid in the Caribbean
A smart-grid project combining PV generation and battery storage has been unveiled in Haiti. The project is the result of collaboration between the Biohaus Foundation and relief organization NPH Germany. The project will substantially reduce the nation’s reliance on diesel generators.
UK researchers launch PV generation forecasting tool
A team of researchers at the University of Sheffield has developed a service to forecast energy generation levels from PV up to three days in advance, allowing grid operators to make decisions further in advance, lowering costs and increasing the efficiency of electricity systems.
Researchers create solar cell and inverter in single device
Researchers from Spain based organization nanoGUNE have developed a solar cell which, through the use of magnetic electrodes, is able to serve as its own inverter.
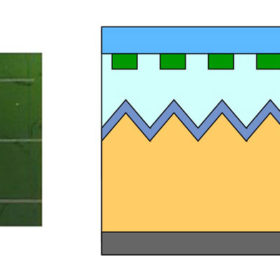
Researchers one step closer to efficient, colorful solar panels
Researchers at the Netherlands’ AMOLF Institute have developed a method for imprinting solar panels with silicon nanopatterns that scatter green light back towards the observer.