Australian manufacturer bets on lithium-titanium-oxide batteries
Zenaji, an Australian manufacturer of lithium-titanium-oxide (LTO) batteries, says the LTO market will hit $5.8 billion by 2032, growing at a 12.6% annual rate. It claims that its Eternity battery system is poised to capitalize on the trend.
Field manual for off-grid residential PV in remote communities
A research team has constructed a technical field audit among users of solar systems in remote communities in Ghana and has identified some recurring technical issues. Based on the collected data, the scientists have also developed a practical field manual.
Enphase Energy, Octopus Energy announce smart tariff for UK customers
In an update to the two companies’ strategic partnership, Octopus customers with Enphase solar and battery systems can now benefit from a smart import and export tariff designed to save money on electricity bills.
EMPA develops biodegradable fungi battery
A team from the Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science and Technology (Empa) has developed a 3D-printed battery. Fungi are used as anode and cathode with one releasing electrons during metabolism and the other able to absorb them.
Toshiba unit launches EneHub platform to support renewable transactions
Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions Corp. has launched its EneHub platform, a web-based service designed to connect renewable energy producers with buyers. It says the solution will facilitate power purchase agreements (PPAs) and simplify energy transactions.
Trump’s $500 billion AI data-center project expected to be powered by solar
US President Donald Trump’s $500 billion AI data-center project, Stargate, could be powered in part by solar and energy storage from Softbank’s SB Energy, says Bloomberg.
The Hydrogen Stream: 41 hydrogen projects to start in Africa by 2029
The Energy Industries Council (EIC) says 41 hydrogen projects are set to begin development across Africa in the next five years, led by North African nations like Egypt, Algeria, and Morocco.
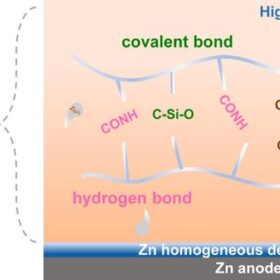
High-voltage, super-stable sodium–zinc hybrid batteries
Researchers from the China University of Petroleum have synthesized a novel hydrogel electrolyte that, when paired with a Prussian blue cathode, achieves outstanding energy density and cyclability in sodium-zinc hybrid ion batteries.
India’s NHPC awards 1.2 GW of solar with storage at $0.036/kWh
NHPC has allocated 1.2 GW of solar with 600 MW/1,200 MWh of storage projects at an average tariff of INR 3.09 ($0.036)/kWh.
Moldova launches tender for 75 MW of battery storage
The procurement aims to improve the reliability of Moldova’s grid, facilitate energy trade with neighboring Romania and Ukraine, and support the integration of locally produced renewable energy.