AE Solar releases bifacial solar modules for vertical projects
AE Solar has launched bifacial solar modules with 560 W to 580 W of power output, designed for vertical installations and agrivoltaic projects. The German company says the modules offer up to 10% backside power gain.
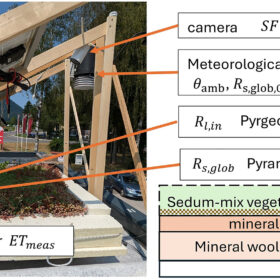
The effect of PV modules on green roofs
Scientists have used simplified 2D view factor and advanced 3D approach to calculate energy fluxes on green roofs with PV systems. They have also constructed an experimental setup to verify their model and have found that without the detailed model, evapotranspiration would be underestimated by 18%.
Trina, Daidohant launch new load-bearing mounting solution for heavy snowfall
The Chinese manufacturer has collaborated with Japan’s Daidohant on the new product. It reportedly suppresses deformation with a special bar attached to the back of the solar module.
Coupling solar-air source heat pumps with sand-based thermal storage floor
Scientists in China have analyzed the performance of a system linking a solar-air source heat pump heating system to sand-based thermal storage floor and have found it can maitain an average indoor temperature of 18.8 C, even when outdoor temperatures range from −18.4 C to 12.3 C.
Turbo Energy launches residential storage solution
The Spanish company says its new storage system has a capacity ranging from 2.4 kWh to 9.6 kWh and a depth of discharge of 90%.
New technique to predict solar inverter temperature
An international research team has developed a novel approach for predicting inverter temperature through symbolic regression based on particle swarm optimization.
New method to identify best locations for offshore hybrid PV-wind projects
Scientists in Spain have created a new index that reportedly help project developers identify better areas in initial stages of hybrid wind-solar power plants development. The proposed approach is claimed to avoid deficiencies of previous criteria and overestimation caused by time delays.
The impact of wind load effects on offshore floating photovoltaics
Researchers have investigated the aerodynamic performance of a single floating PV setup of 16 panels, as well as an array that combined 15 such setups. They found that drag coefficient distributions and wind pressure effects on PV systems vary by inlet angle. They have also identified cost-saving opportunities through material optimization.
Fronius introduces 15.8 kWh lithium iron phosphate battery for rooftop PV
The Austrian manufacturer has launched its first battery system using LFP cells. A total of up to four units can be connected in parallel for a capacity of 63 kWh.
The impact of different substrates on solar module performance
A research team has analyzed the effects of different substrates on PV module performance and has found that ground soil achieves the highest efficiency at 21.1%, followed by grass (19.6%), wood (17.95%), concrete (16.2%), roof tiles (14.3%), and iron sheets (11.5%).