PVcase introduces AutoCAD tool for rooftop solar systems
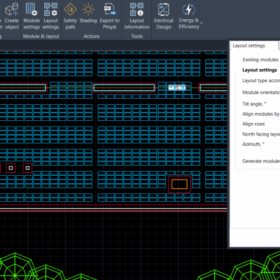
PVcase has introduced a new AutoCAD tool for rooftop PV systems, featuring 3D building preparation, layout generation, shading calculation, and electrical design capabilities.
JinkoSolar introduces all-in-one battery solution for C&I solar
JinkoSolar has launched an all-in-one battery solution for commercial and industrial (C&I) solar applications. It includes a new outdoor cabinet that integrates battery packs, a management system, a power conversion system, and firefighting equipment. The system offers 215 kWh of battery capacity and up to 100 KW of rated power output.
Hybrid PV-biogas microgrids for EV charging
An international research team has examined the potential use of hybrid microgrids that integrate PV and biogas for electric vehicle recharging in Karnataka, India. Their findings indicate that this combined approach offers economic and environmental benefits compared to separate biogas and PV systems.
Optimization model to integrate heat pumps in non-continuous industrial processes
The new optimization method is intended at designing smaller and cheaper heat pumps. Its creators said the new approach also enables higher Opex savings and an improved coefficient of performance.
Ireland introduces online tool to calculate rooftop PV potential
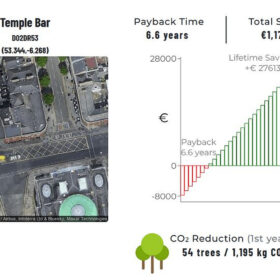
The Irish Solar Energy Association and AirPV have developed an online tool to calculate rooftop solar potential, enabling homeowners and businesses to estimate payback times, annual savings, and emission reductions.
High resolution satellite imagery for residential PV system detection
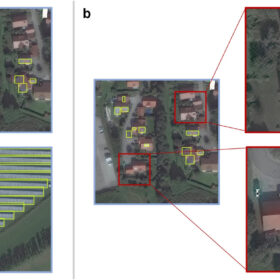
US-based Maxar Technologies used satellite imagery imagery with resolution of 31 cm to 15.5 cm to identify rooftop PV systems in southern Germany. The company claims its new approach was able to identify 97.8% of the solar arrays with high confidence.
New model for day-ahead solar forecasting in areas with limited data
South Korean researchers have developed a long-term solar irradiance prediction method based on a reinforcement learning algorithm. They claim that the new model is able to forecast solar radiation for more than a year using just two weeks of solar radiation learning.
European research group creates injection molding plastic solar cells
A French-Spanish research team developed organic photovoltaic modules embedded into plastic parts through high throughput injection molding. The researchers injected thermoplastic polyurethane in the modules and found it enhances their mechanical stability while keeping a high flexibility.
Techno-economic dispatch model to combine pumped hydro with solar, wind power
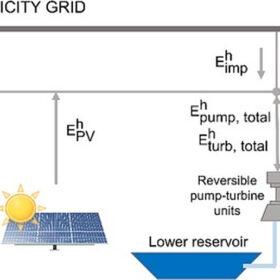
A research team in Spain has developed an hourly mathematical model that reportedly allows for the optimal management of grid-connected renewable generation facilities and pumped hydro-energy storage with reversible pump turbine. The scientists tested the model on a potential pumped hydro-solar-wind complex in northern Spain and found that the combination of the three technologies may achieve considerable savings.
Wind speed increases could cause PV yield losses
A Spanish research group says air flux variations over different parts of solar plants could also lead to mismatch losses. Past. studies have only looked at the benefits of high wind speed on PV arrays, which enhances module cooling.