German firm offers 400 W solar table
Technaxx, a German firm, has developed a 400 W solar table that combines the functionality of an outdoor table with a power generation unit, using PERC technology for its solar modules.
New research helps identify optimal cleaning cycle to reduce soiling in MENA region
Researchers in Oman have investigated the effects of soiling on solar module performance and have found that between 8 and 12 cleaning cycles may be enough to ensure higher energy yields.
Logistics company testing PV-powered electric truck for remote locations
Gebrüder Weiss is testing electric trucks with two electric motors and 7.4 kWp of PV output. The modules are installed on the top of the trucks and as mobile extensions.
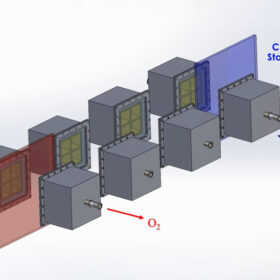
MIT scientists develop CSP system to produce hydrogen
Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) scientists have developed a train-like concentrated solar power (CSP) system for hydrogen production, with plans to build a prototype in the coming year. They say that this innovative system can capture up to 40% of the sun’s heat to produce environmentally friendly hydrogen fuel.
Atess releases new 1 MW battery inverter
Chinese manufacturer Atess has developed PCS1000, a 1 MW bidirectional battery inverter for commercial and industrial applications, with a 99% efficiency rating.
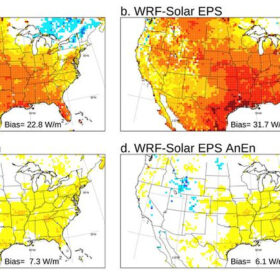
New research points to WRF-Solar forecast shortcomings
A research team in China assessed the accuracy of the WRF-Solar numerical weather prediction model in simulating global and diffuse radiation. The group’s work highlighted the model’s sensitivity to aerosol optical depth, cloud optical thickness, and solar zenith angle.
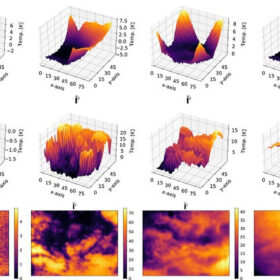
Bismuth ferrite, tungsten trioxide thin films for PV cells
Researchers recently identified the optimal laser energy for crafting BFO/WO3 bilayer thin films for solar cells at 200 millijoules (mJ), by carefully considering factors such as leakage and band gap.
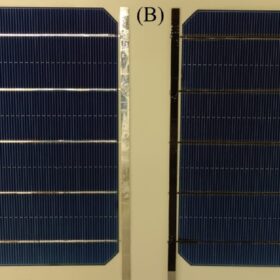
Coating metallic ribbons for aesthetic implementation of BIPV
Researchers in Switzerland have looked into three kinds of black ink coating for metallic ribbons used in PV modules. They have compared their visual stability and their effect on electrical performance.
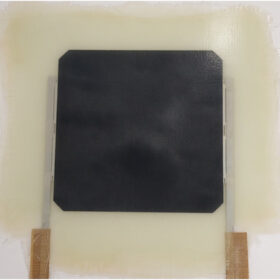
Novel solar module encapsulant based on glass-fiber, epoxy resin
Researchers in Spain have used a glass fiber reinforced composite material with an epoxy matrix containing cleavable ether groups as an encapsulant material for photovoltaic panels. They found that new material still has issues with performance stability, but they also ascertained it ensures lower electrical losses.
Integrating sky images, global solar irradiance into solar forecasting algorithms
A research team in the United States has created a novel approach to integrate raw sky images and global solar irradiance measurements, solar nowcasting, and intra-hour forecasting. The methodology utilizes low-cost radiometric IR cameras instead of expensive ceilometers.