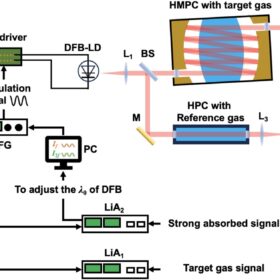
Hydrogen detection system for safety, quality control
Researchers in Japan have developed an optimized hydrogen gas measurement using TDLAS technique. It is reportedly able to achieve a detection range of hydrogen gas concentration of 0.01% to 100%. The group said that it can improve hydrogen safety and in turn, its adoption.
Research shows tilt angles over 30 degrees delay solar module thermal failures
A Chinese-Italian research team has analyzed the influence of different tilt angles on the thermal failure of the photovoltaic façades or roofs in fire conditions, finding that when the tilt angle exceeds 30 degrees, the time to failure increased significantly.
3D-printed anti-reflective cover based on aluminium oxide increases PV cell efficiency by 25%
An international team of scientists have combined cyclic-olefin copolymers with a powder of aluminum oxide to create a filament that can be used by a 3D printer to create anti-reflective covers for PV modules. The proposed innovation can reportedly improve PV cell efficiency by over 25%.
Leclanché releases battery cell with niobium-based anode material
The Swiss manufacturer said the cell was developed in partnership with Echion Technologies, which supplied the niobium-based active anode material. It has greater energy density and faster charging compared to LTO technologies.
Controlling grid fluctuations via solar module cooling
A research group has proposed a novel method to control ramp rates in power networks. Its control optimization is based on weather, load and production forecast data. The scientists simulated the operation of the proposed technique and reached a ramp rate reduction of up to 76.2%.
Metrel launches electrical installation safety tester for PV systems
Metrel, a Slovenian measurement equipment supplier, says its new electrical installation safety tester can assess systems with a maximum voltage of up to 1,500 V and a maximum short circuit current of 40 A.
Huasun to supply 1 GW of HJT products to Xinjiang Silk Road, annually
The Chinese company said that, under a new agreement, it will collaborate with Xinjiang Silk Road to produce high-efficiency HJT PV modules. It will supply silicon wafers, cells, modules, and more.
Greek researchers develop privacy-preserving PV forecasting technique
Researchers from Greece have developed a PV forecasting technique for prosumer schemes using federated learning, a machine learning method that sends local model updates to a central server for correction. Their simulations show surprising results compared to centralized forecasting.
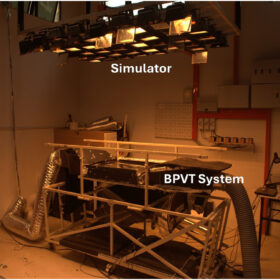
Cooling bifacial PV thermal solar panels with jet impingement
Scientists created a model to study bifacial PV thermal (BPVT) solar panels using jet impingement and built an experimental setup to validate it. They achieved a thermal efficiency of 62.28%, while electrical efficiency peaked at 11.22%.
Researchers analyze wind cooling effect for 5.9 MW rooftop PV array
Researchers have analyzed how wind speed and direction affect the cooling of a rooftop PV plant with 10,806 panels. They say that winds from behind were less effective due to the roof slope and the minimal gap between the panels and the roof, but wind from other directions could contribute to a cooling effect of up to 7 C.