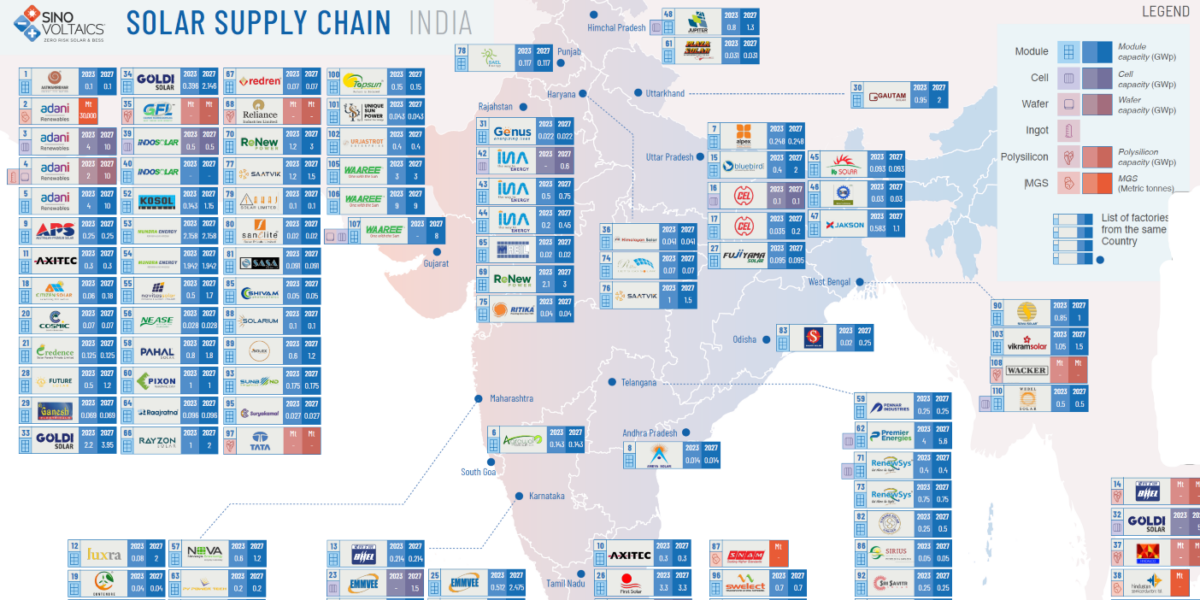
Hong Kong-based quality assurance company Sinovoltaics has published its India Solar Supply Chain Map for the fourth quarter of 2024, indicating 58.4 GW of module capacity with a further 60 GW to be added between 2027 and 2030, enabling a total of 119 GW.
The analysts pointed to the “Make in India” and production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme as key drivers of the expansion. They noted that the maps are based on announced initiatives tracked by Sinovoltaics' team.
As for technology trends, the report said that most of the production is focused on passivated emitter rear contact (PERC) technology with a “clear shift towards tunnel oxide passivated contact (TOPCon)” underway.
The cell production nameplate capacity is at 13.6 GW, with an announced increase of 47.2 GW in the coming 3 to 5 years for a total of 61.6 GW by 2027/2030. The ingot capacity figure reported was 4 GW with 28 GW announced for the 2027/2030 period, according to the analysts.
They also highlighted the addition of Maharashtra-based Luxra Solar India's plan to add 2 GW of module production by 2027/2030, also that there are five fewer production sites compared to the previous report due to the decision to leave out building integrated PV (BIPV) module manufacturers.
The report is free to download.
Covering manufacturing hubs in East Asia, Europe, and North America, the Sinovoltaics solar supply chain maps are published quarterly, and are meant to support traceability research. They include details about the size, location, owner, and capacity, including PV modules, cells, wafers, ingots, polysilicon, and metallurgical-grade silicon manufacturing sites. The details are based on press releases and data gathered by Sinovoltaics.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.


By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.