Germany-based Webasto, a developer of vehicle-integrated photovoltaic (VIPV) solutions and an automotive industry supplier, unveiled a new car roof system concept designed to be able to generate 350 kWh of electricity per year and reduce the roof system's weight by up to 40% compared to conventional designs.
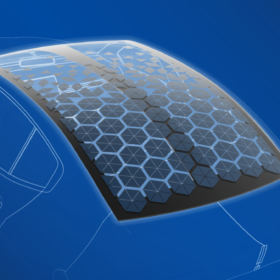
The novel PV roof concept, dubbed EcoPeak, is a VIPV system that covers the rear window and roof area, made with triangle-shaped silicon solar cells arranged in a honeycomb matrix pattern. The enlarged surface area reportedly enables up to 2,500 km more range per year, depending on the vehicle and local climate conditions, according to Webasto.
“The solar cell design and panel design were done by Webasto internally by our R&D department. But it was not just an abstractive design activity, we also investigated possible suppliers for a hardware buildup of this concept in the future,” Maximilian Hofbeck, director of product management and sustainability, told pv magazine.
The EcoPeak concept is meant to enable automotive manufacturers to focus either on sustainability or aesthetics or a combination of both, according to Jan Henning Mehlfeldt, board member and responsible for Webasto global automotive roof business. For example, if the focus is on efficiency, then the cells can be placed across the entire surface without any spaces in between. Alternatively, fewer cells and more space for different shapes could enable more comfort or natural light in the cabin
In the past, Webasto has used conventional passivated emitter rear contact (PERC) solar cells to make 300 W sun roofs for electric sport utility vehicles. “The Fisker Ocean is a perfect example: the large openable solar roof from Webasto is a real eye-catcher and makes sustainability perceptible,” said Mehlfeldt.
Another feature of the EcoPeak concept is that it uses polycarbonate material made from biomass-balanced and recycled materials rather than aluminum which makes it reportedly 40% lighter, according to the manufacturer.
The European Chemical Industry Council defines the biomass balance method as a technique developed by BASF to use bio-naphtha or biogas derived from organic waste or vegetable oils to partially replace fossil resources to produce chemicals and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, while maintaining product quality.
When asked about the chances of the EcoPeak innovations making it into commercial products, Mehlfeldt told pv magazine, “Internal developments are running for all our roof systems and we are looking closely at the components and sustainable alternatives. Here we use insights of the EcoPeak to offer a wide range of sustainable solutions for the customer-specific demands.”
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.




2 comments
By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.