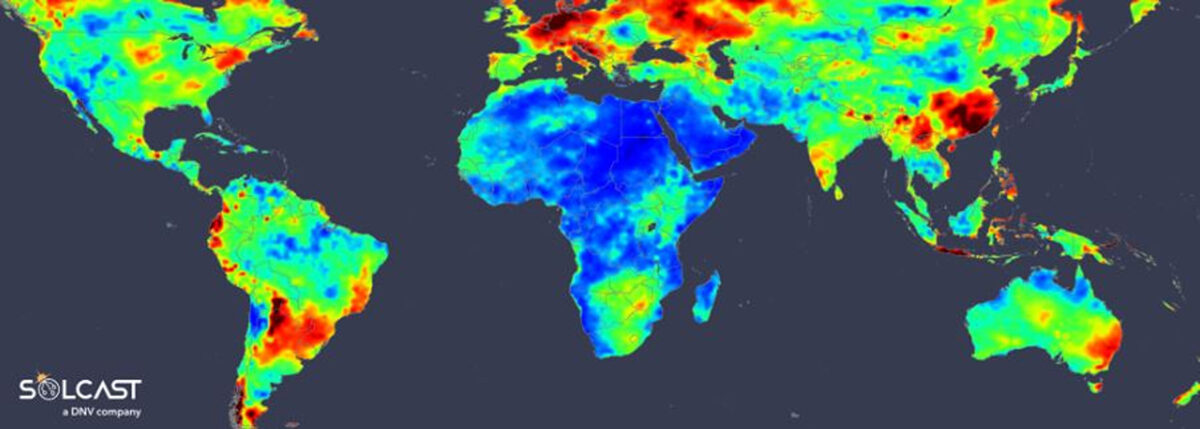
Understanding the year-to-year variability of solar energy potential is vital for grid planning and optimizing storage. An analysis using the Solcast API reveals regions with the most significant differences in irradiance from year to year. This data was constructed by looking at the decadal variability, comparing the range of the total yearly irradiances to the average irradiance at each location. Interestingly, regions with high intra-day variability in cloud are not necessarily those with the biggest inter-year variability.
The regions with the highest year-to-year variability in irradiance include Central and Northern Europe, East Coast Australia, Northern Argentina, and China. Africa exhibits the most stable irradiance year-on-year.

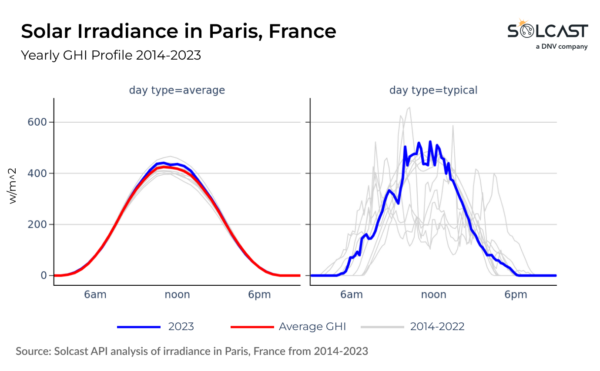
In Central and Northern Europe, high irradiance variability is driven by the dominance of either the continental air masses to the South and East or the maritime air masses from the Atlantic, Arctic, and Mediterranean. The Iberian Peninsula, however, experiences less variability due to a relatively consistent mixing of Atlantic and Mediterranean air masses.
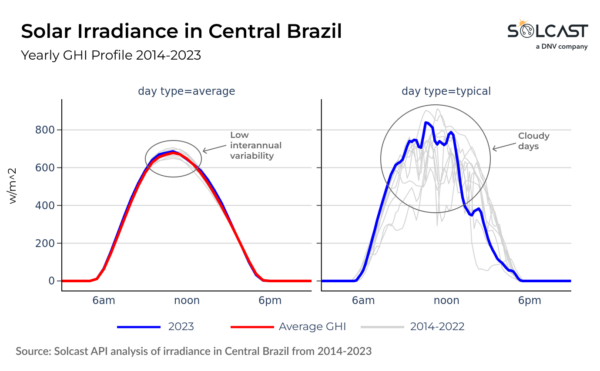
The year-to-year and intra-day variability can be seen for individual locations by comparing average and typical days from each year. The former shows the range of variation in annual values, represented as an average day, and the latter uses real representative days to show cloud variability in irradiance.
North America presents moderate variability in the Gulf Coast, Midwest, and Northeast regions, influenced by the interaction of Gulf of Mexico moisture, eastward-tracking Pacific frontal systems, and Atlantic air masses. In comparison, the Rockies and West Coast show
comparatively stable year-on-year irradiance, dominated by westerly airflow from the Pacific.

South America shows a contrasting scenario. Despite high daily variability due to cloud and rainfall, the Amazon region maintains a surprisingly consistent amount of cloud cover year-on-year, resulting in stable total annual irradiance. The Atacama Plateau, similar to
Saharan Africa, is exceptionally stable due to minimal cloud cover. In Northern Argentina, large swings in interannual irradiance are observed, depending on how Pacific frontal systems interact with the Andes mountain range.
In India, the western region's total irradiance varies year-on-year due to a less regular and consistent monsoon compared to the east. China's large irradiance variability is partly driven by changes in aerosol loads over the past decade, with eastern Asia experiencing moderate year-on-year variability.
Saharan Africa and the Middle East exhibit the least variability in interannual irradiance, dominated by cloud-free desert conditions. Sub-Saharan Africa, despite a tropical wet season, remains fairly consistent from year to year. However, Southern Africa experiences more variability due to the interaction between tropical and mid-latitude weather systems.
The Sunda Islands of Indonesia exhibit high variation in irradiance due to shifts in the Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) and the Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD), which can drastically affect the intensity and duration of the bi-annual wet seasons.

East Coast Australia experiences high variation due to teleconnections with the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO), which also influences variability along the north-west coast of South America. Central Australia's deserts are less consistently sunny compared to other deserts, such as the Sahara, Middle East, and Atacama Plateau due to ENSO's impact. In contrast, northern tropical Australia has relatively stable irradiance between years due to the moderating influence of a consistent dry season outweighing the wet seasons' variability.
Solcast produces these figures by tracking clouds and aerosols at 1-2km resolution globally, using satellite data and proprietary AI/ML algorithms. This data is used to drive irradiance models, enabling Solcast to calculate irradiance at high resolution, with typical bias of less than 2%, and also cloud-tracking forecasts. This data is used by more than 300 companies managing over 150GW of solar assets globally.
The views and opinions expressed in this article are the author’s own, and do not necessarily reflect those held by pv magazine.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.


By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.