From pv magazine USA
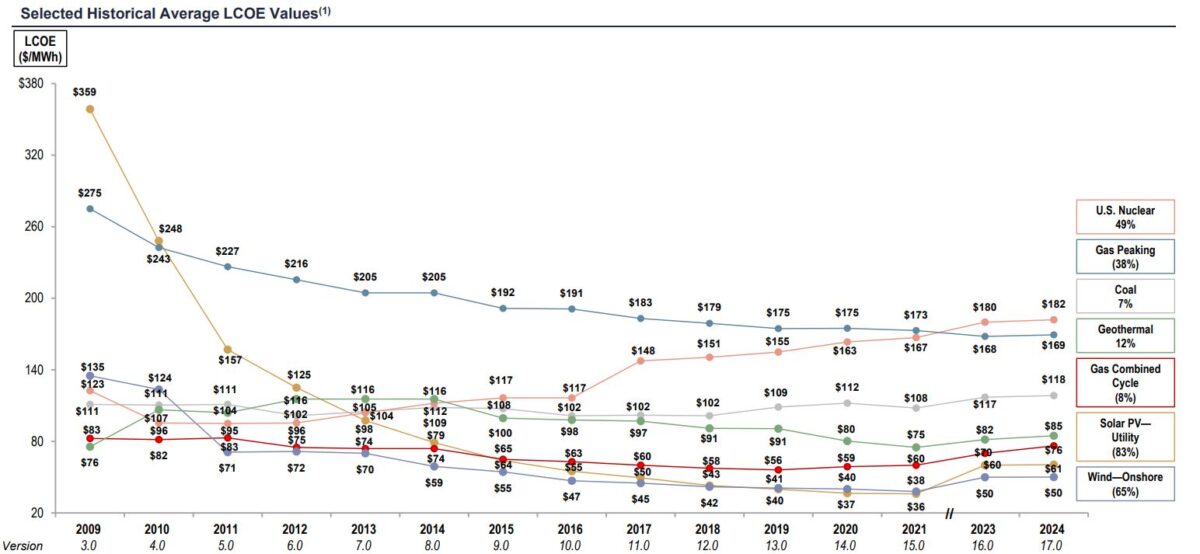
Lazard has released a report analyzing LCOE, a critical measure of cost-efficiency of generation sources across technology types. The report found that onshore wind and utility-scale solar have the lowest LCOE by a large margin.
LCOE measures lifetime costs divided by energy production and calculates the present value of the total cost of building and operating a power plant over an assumed lifetime.
“Despite high end LCOE declines for selected renewable energy technologies, the low ends of our LCOE have increased for the first time ever, driven by the persistence of certain cost pressures (e.g., high interest rates, etc.),” said Lazard. “These two phenomena result in tighter LCOE ranges (offsetting the significant range expansion observed last year) and relatively stable LCOE averages year-over-year.”
Onshore wind ranked as the lowest source of new-build electricity generation, ranging from $27/MWh to $73/MWh. Utility-scale solar was a close second, ranging $29/MWh to $92/MWh.
Utility-scale solar has had the most aggressive cost reduction curve of all technologies, falling about 83% since 2009, when new-build solar generation had an LCOE of over $350/MWh.

Solar at the utility-scale is far lower in cost than the LCOE of coal, the least-expensive source of fossil fuel generation. Coal LCOE ranges $69/MWh to $169/MWh, making it nearly double the average LCOE of utility-scale solar assets.
Meanwhile, natural gas peaker plants are highly inefficient in LCOE, ranging from $110/MWh to $228/MWh. Nuclear energy had the highest utility-scale LCOE with an average of $182/MWh.

LCOE is a powerful measure to compare technology cost efficacy, but it does not tell the whole story. For instance, research from the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory found that wind and solar generation provided $249 billion dollars of climate and air quality health benefits from 2019 through 2022, or over $62 billion annually.
While utility-scale solar had the lowest LCOE, costs for smaller-scale distributed solar projects have fallen as well. Community, commercial, and industrial scale projects ranged $54 to $191 per MWh. Residential solar ranged $122/MWh to $284/MWh, making it a more expensive source of generation.
However, LCOE does not consider cost benefits like the lessened need for long-distance transmission buildout that occurs from distributed rooftop solar buildout. Environment America released a report assessing the co-benefits of rooftop solar, which can be found here.
Lazard also analyzed the cost impacts of the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), which includes both generation-based Production Tax Credits, and project-based Investment Tax credits for renewable energy assets. The chart below models the cost impact on these technologies, as seen below.

Energy storage saw cost improvements from the IRA as well. The levelized cost of storage (LCOS) for a utility-scale, 100 MW, 4-hour storage system ranged $170/MWh to $296/MWh pre-IRA. Post-IRA, the low-end of the LCOS range landed at $124/MWh.
Find the full ninth annual report from Lazard here.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.



Please choose different colors for the graphs