Microgrids, which are originally designed for predefined load demands, face vulnerabilities when accommodating additional demands such as electric vehicles (EVs). Merging renewable energy resources, energy storage, and EVs in a residential setting frequently brings challenges, such as overload or surplus generation, and creates dispersed microgrids, which are vulnerable if operated individually.
To tackle these issues, researchers from the University of Technology Sydney, Deakin University and Murdoch University in Australia have developed a reconfigurable multi-microgrid system that can better respond to the changing load profiles by leveraging the power of V2G technology, as well as create techno-economic benefits for distribution network service providers (DNSPs), such as minimizing the curtailment in load and surplus generation in microgrids.
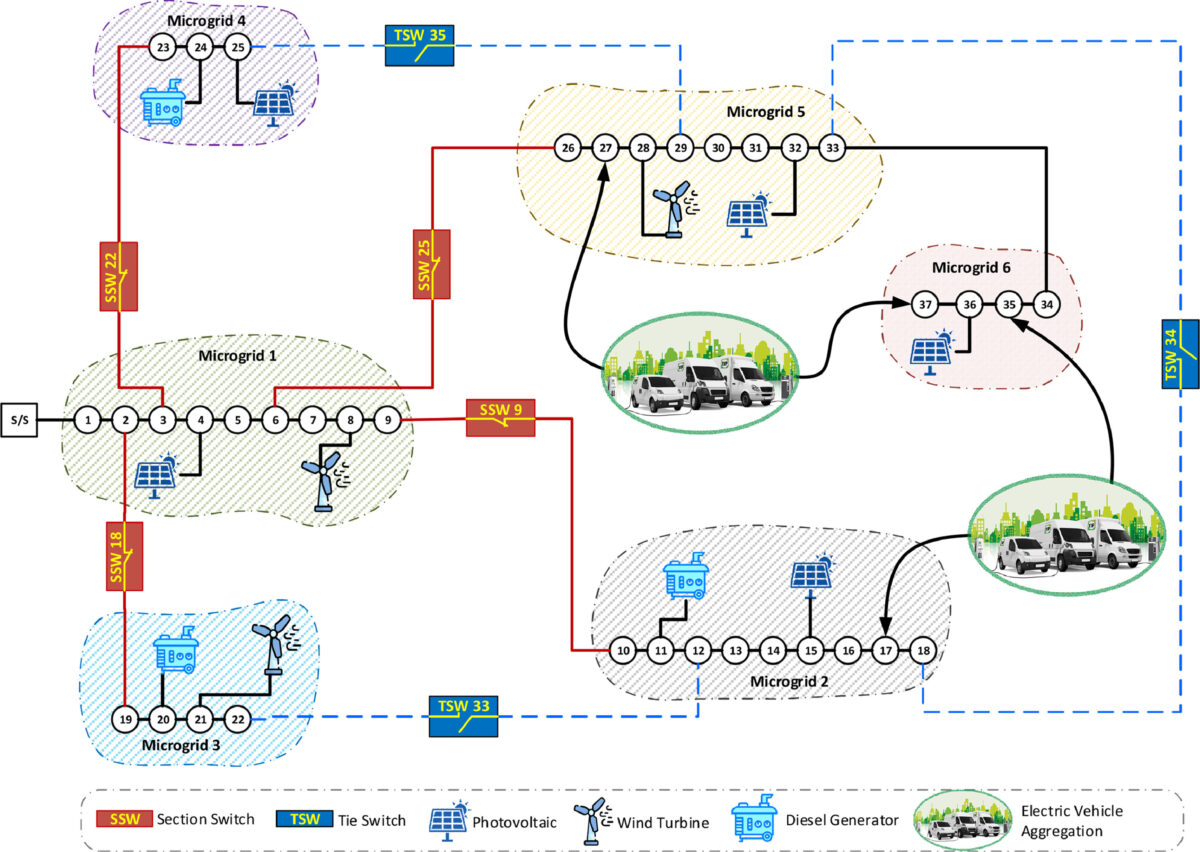
The research focuses on interconnecting a group of scattered microgrids to create a multi-microgrid system. By developing an energy management strategy to reconfigure the interconnections among microgrids, the researchers have facilitated the efficient exchange of power among these multi-microgrid systems, addressing the variability in load demands in the face of intermittent generation of renewable generation. To further enhance the flexibility of the model, they have also integrated grid-to-vehicle (G2V) and V2G concepts.
The proposed approach, characterized by its mathematical convexity, allows distributed network service providers (DNSPs) to utilize commercial platforms like CPLEX and GUROBI, which can in turn enable them to find feasible solutions more effectively, with minimal computational burden. The effectiveness of the proposed method is demonstrated through its implementation on a modified 33-bus test system operated as multi-microgrid system.
“The results show the effectiveness of the proposed approach as a promising tool for optimizing the operation of reconfigurable multi-microgrid systems in the presence of electric vehicle aggregations (EVAs), leading to operational cost reduction and voltage profile enhancement,” the researchers stated.
Their findings are discussed in the paper “Stochastic scheduling of energy sharing in reconfigurable multi-microgrid systems in the presence of vehicle-to-grid technology,” which was published in the journal Electric Power Systems Research.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.



By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.