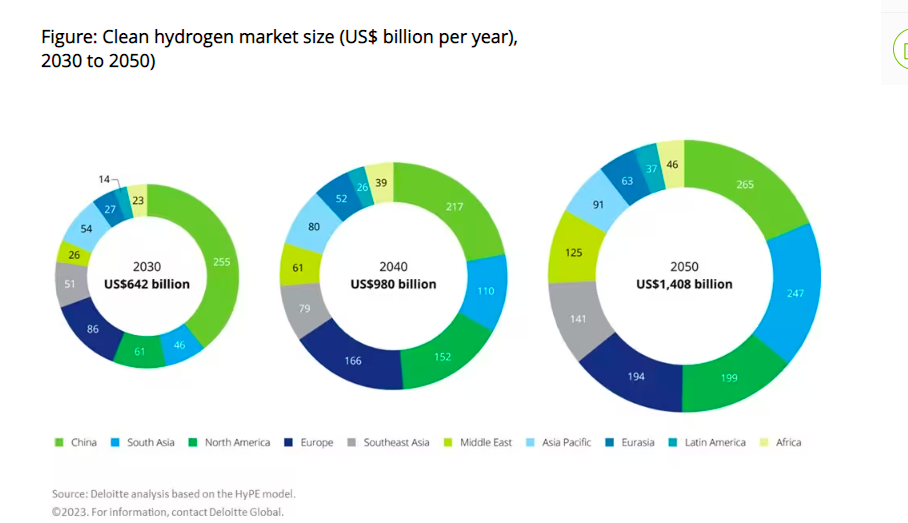
Deloitte predicts that the hydrogen market will surpass the value of the liquid natural gas trade by 2030, reaching $642 billion in annual revenue and growing to $1.4 trillion per year by 2050. According to the consultancy, global trade and diversified transport infrastructure are crucial for unlocking the full potential of the green hydrogen market. Deloitte's outlook suggests that by 2050, major regions engaging in global trade could generate over $280 billion in annual export revenues. In 2030, Asia is expected to capture 55% of the market, driven by soaring demand in China, India, and Indonesia. The report notes the need for more than $9 trillion of cumulative investments in the global clean hydrogen supply chain to achieve net-zero compliance by 2050. It also says that clean hydrogen presents a significant sustainable growth opportunity for developing countries.
Dutch Prime Minister Mark Rutte and Danish Prime Minister Mette Frederiksen met with Namibia's President Hage Geingob to discuss energy cooperation. The purpose of their visit is to explore opportunities for signing energy agreements with Namibia, particularly in relation to the country's multibillion-dollar green hydrogen projects. Rutte noted their intention to enhance cooperation on green hydrogen, accompanied by companies and knowledge institutions. Additionally, the two European leaders are visiting South Africa and Morocco to engage in discussions about hydrogen collaboration. In May, Namibia initiated the feasibility stage of the green hydrogen project through an agreement with Hyphen Hydrogen Energy.
University of Alberta researchers have studied small modular nuclear reactor power plants (SMNRPPs) and their influence on hydrogen supply costs. Their findings indicate that in electricity markets with high fossil fuel-dependence, hydrogen supply costs can range from CAD 1.77/kg ($1.34/kg) to CAD 3.36/kg, while in low fossil fuel-dependence markets, the range is estimated to be CAD 2.11/kg to CAD 2.77/kg. Their analysis, outlined in the paper “Assessing the cost competitiveness of electrolytic hydrogen production from small modular nuclear reactor-based power plants: A price-following perspective,” involved combining economic dispatch and leveled cost analysis models. The researchers also considered the adaptability of SMNRPPs to adjust power output based on fluctuating electricity market prices. They emphasized that the SMNRPP-electrolysis system proves more cost-effective than fossil fuel-based hydrogen production at a capital cost decrease of CAD 4,700/kW, with the capital cost accounting for 75% of the hydrogen supply cost variance. The study was published in Applied Energy
Iqony Energies has announced its intention to construct a 53 MW electrolysis plant in Saarland, Germany. The company aims to facilitate the decarbonization of industries in the region, including the steel industry and the mobility sector. Anke Langner, managing director of Iqony Energies, said that waiting for a sufficiently efficient European hydrogen pipeline network could hinder the industry's rapid adoption of hydrogen.
Everfuel has initiated a controlled venting process for all hydrogen trailers from the same supplier after detecting a malfunction and leak in one of its 12 trailers. The initial investigation report pinpointed a valve as the cause of the leak and acknowledged the possibility of it being a systemic issue.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.


1 comment
By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.