Bslbatt unveils 90-mm-thick battery for residential solar
China’s Bslbatt said its new product has a storage capacity of 5 kWh and a nominal voltage of 51.2 V. It measures 670 mm x 540 mm x 88 mm and is 90 mm thick.
Woodside selected to deliver green hydrogen megaproject in New Zealand
Australia-based Woodside Energy has beat Fortescue Future Industries for the opportunity to deliver the proposed 600 MW Southern Green Hydrogen megaproject in New Zealand. It will produce green hydrogen for export using power from partner Meridian Energy’s hydroelectric plant.
Brick-and-iron heat battery for zero-carbon industrial processes
Bill Gates-backed Rondo Energy has released the “brick toaster” heat battery, which stores renewable energy and dispatches heat and electricity for steel, cement, and chemical production.
Rooftop system with PV panels, mini wind turbines in the Netherlands
Ibis Power has developed a rooftop system that combines solar with wind turbines designed for medium-sized structures and high-rise buildings. It claims its PowerNEST system can produce six to 10 times more energy than standalone rooftop solar. The company has already installed five projects in the Netherlands.
China’s PV capacity hits 364.4 GW
IEA-PVPS says that China added around 58 GW of new PV capacity in the first 10 months of the year, bringing cumulative installations to 364.44 GW. It says up to 100 GW of new capacity could be deployed by the end of this year.
Colbun switches on battery-linked 230 MW solar plant in Chile
Colbun has completed the Diego de Almagro Sur solar plant in Chile’s Atacama region. It is connected to 8 MW/32 MWh of battery storage.
Mitsubishi unveils air source heat pump
Mitsubishi has released a cascaded air source heat pump that can produce between 7.8 kW and 640 kW of heat. It is reportedly able to generate hot water at a temperature of up to 70 C without boost heaters.
The Hydrogen Stream: Green hydrogen via ammonia decomposition
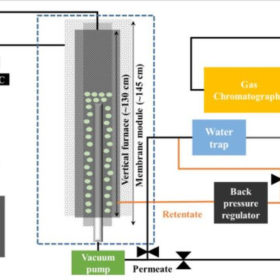
South Korean scientists have developed a highly selective palladium composite membrane on porous metal supports to cut the ammonia content of the permeated hydrogen stream. Dutch researchers, meanwhile, have presented two alternatives to this strategy – increasing the thickness of the membrane selective layer, or using a purification unit in the permeate of the membranes.
Chinese PV Industry Brief: TCL Zhonghuan cuts wafer prices by more than 4%
TCL Zhonghuan has announced wafer price cuts, Shenzhen Energy unveiled a plan to build a 2 GW solar-storage project, and the Chinese authorities have announced measures to expedite grid connections for new solar and wind plants.
Netherlands changes grid code to reduce congestion, host more renewables
New rules in the Netherlands will allow new entities known as “congestion service providers” as intermediaries between grid operators and power plant operators, in order to make optimal use of the network.