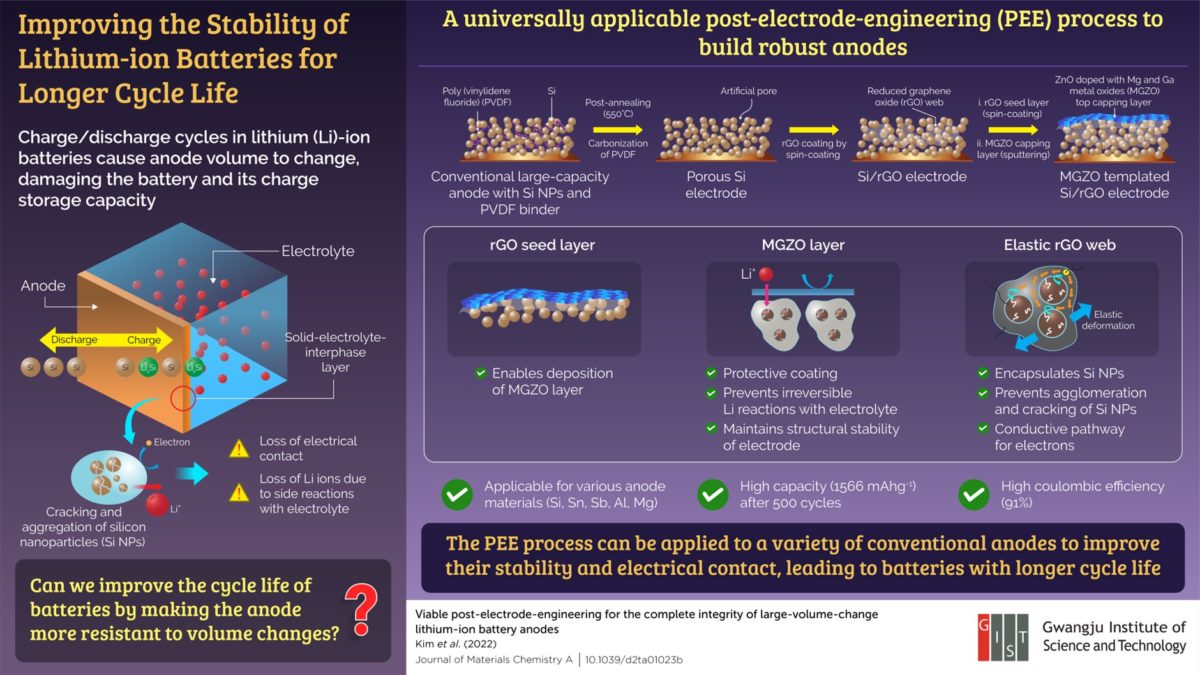
Charge and discharge cycles in lithium-ion batteries cause anode volumes to change, reducing battery capacity and cycle life. Now, researchers at GIST in South Korea have developed a new way to strengthen the anode and modify it, regardless of its material or how it is manufactured.
Over time, charging and discharging causes the nanoparticles in the anode to crack and cluster together at the electrode-electrolyte interface. This leads to an electrical disconnection, reducing the amount of charge the anode can store or transport. To address this issue, GIST researchers have developed a method to make the anode more resilient against volume changes by encapsulating the nanoparticles in an elastic web-like structure.
The researchers described in Journal of Materials Chemistry A how they used a conventional anode containing silicon nanoparticles held together by a polymer (polyvinylidene fluoride) binder. To accommodate the web-like structure, they removed the binder by heating the anode using an annealing process.
The gap between the nanoparticles was then filled in with reduced graphene oxide (rGO) solution, which dried up to form a web that held the silicon nanoparticles together and prevented them from cracking. Additionally, the web provided a conductive pathway for the electrons, allowing the nanoparticles to bind with lithium.
The researchers used a technique called “spin coating” to coat the anode surface with rGO. The rGO coating served as a seed layer for the deposition of a protective layer consisting of zinc oxide with magnesium and gallium metal oxides added to it (MGZO). This MGZO layer provided structural stability to the anode.
“The structure retained a high storage capacity of 1566 mA h g-1 after 500 cycles and showed 91% coulombic efficiency, which relates to the battery life. This could pave the way for electric vehicles that enable us to drive long distances on one-time charging,” said Prof. Hyeong-Jin Kim, who joined GIST after serving as president of LG Chem Michigan.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.



By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.