Australia’s largest planned Renewable Energy Zone (REZ) is to be built in the New South Wales (NSW) northeast with the state government announcing the New England REZ, which will deliver at least 8 GW of new network capacity, has been formally declared.
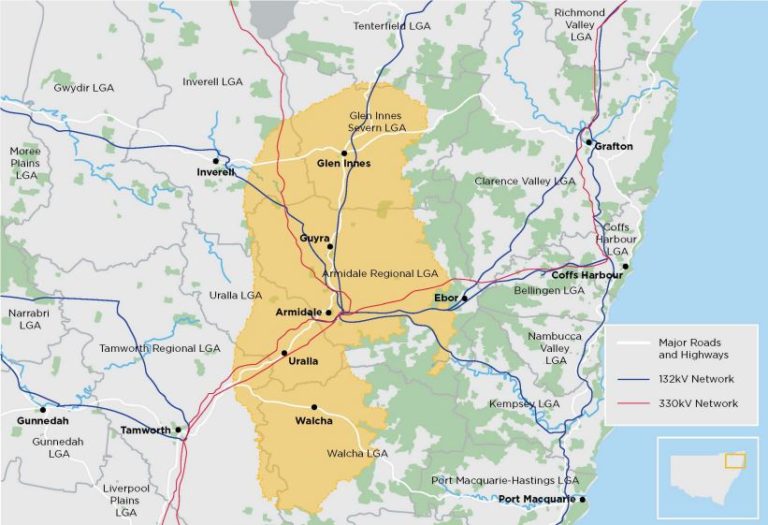
The declaration of the New England REZ is the first step in formalising the coordinated energy zone under the Electricity Infrastructure Investment Act 2020. It sets out the intended network capacity, geographical area and infrastructure that will make up the New England REZ which is centred on the northern city of Armidale and extends west towards Uralla and east to Ebor and takes in Walcha to the south and Glenn Innes to the north.
Energy Corporation of NSW chief executive officer James Hay said the state government is powering ahead and meeting major milestones on its Electricity Infrastructure Roadmap with this REZ, which follows the declaration of the Central-West Orana REZ in November.
“REZs are the modern-day equivalent of a power station, combining low-cost renewables with back-up energy from storage and transmission to deliver cheap, reliable and clean energy,” he said.
“It’s phenomenal to get this REZ declared as New England has some of the best natural energy resources in the country, including some of the state’s best potential sites for pumped-hydro and strong investor interest.”
Energy Minister Matt Kean said the 8 GW New England REZ is the biggest commitment to cheap, clean energy in the state’s history with the NSW Government committing to invest $78.9 million to support its development.
“The New England REZ is a fundamental part of our Electricity Infrastructure Roadmap and we expect it will deliver up to 8,000 megawatts of new capacity, $10.7 billion in private investment, around 830 operational jobs and 1,250 construction jobs to the local economy,” he said in a statement.
“The New England REZ will be able to power 3.5 million homes and, when coupled with Central-West Orana REZ, sets the state up to become the number one destination across Australia for renewable energy investment.”
The New England REZ is set to become the nation’s largest energy zone with a call for registrations of interest (ROI) last year attracting more than 80 new solar, wind and energy storage projects, totalling a massive 34 GW.
Kean said the response to the ROI process showed huge investor confidence in the state’s Electricity Infrastructure Roadmap with more than four times the level of interest needed to build out the planned 8 GW REZ.
“The overwhelming response shows this is a once-in-a-generation opportunity to attract enormous investment into regional areas, cementing NSW’s renewable energy future,” he said.
The New England region has already attracted a host of large-scale wind and solar projects, including the Walcha Energy Project, a 4 GW wind, solar and pumped hydro energy storage hub put forward by Energy Estate and its partners.

Joint venture UPC/AC Renewables Australia has commenced construction of the first 400 MW stage of the New England Solar Farm while Spanish developer Fotowatio Renewable Ventures (FRV) is progressing with the 115 MW Metz Solar Farm.
The state-owned Energy Corporation of NSW (EnergyCo) has been appointed as the infrastructure planner for the New England REZ and will coordinate the generation, firming, storage and transmission projects leading the delivery of the state’s REZs.
Hay said EnergyCo has and will continue to work with a range of stakeholders in the New England region to deliver the REZ in a way that considers local priorities and values, land use planning, investor interest and the legislative requirements.
“This is great news for the region as the REZ will help drought-proof traditional farming communities and provide new income streams for landholders that host electricity infrastructure,” he said.
“It is estimated that in the New England REZ, this could amount to around $660 million in lease payments for landholders to 2042.
“REZs will also play a key role in delivering on our commitment to halve the state’s emissions by 2030 and achieve net-zero by 2050.”

The New England REZ is one of five designated clean energy areas detailed in the NSW Government’s electricity roadmap, which is anticipated will support more than $32 billion of investment in renewable energy generation, storage and transmission in the state.
REZs will also be developed in the Central-West Orana, South-West, Hunter-Central Coast and Illawarra regions and are expected to bring 12 GW of renewable energy and 2 GW of storage online ahead of the planned retirement of the coal-reliant state’s aging thermal-generation fleet with four of its five fossil-fuelled power plants expected to close in the next 15 years, starting with Liddell in 2023-24.
The Central-West Orana REZ, which is tipped to deliver 3 GW of renewable energy, was the first of the REZs to be launched with the call for ROIs last year attracting 113 registrations, totalling 27 GW and valued at $38 billion.
The state government has also invited ROIs from renewable generators, energy storage and network developers, and existing and proposed energy loads, to participate in shaping the South-West REZ, which is centred on the inland town of Hay and extends west to Buronga and east to the fringes of Griffith.
The New England REZ will be built in stages, with the delivery timetable to be developed throughout the planning process.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.



By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.